Availability Set (Server Level Availablity )
The major difference between an Availablity set and an Availability zone is an Availablity set provides HA for the server level in the same data centre and the Availability zone provides HA for the data centre in the same region.
An Availablity set allows “matching” vm (app, DB etc ) to be spread across multiple hosts or racks in the same DC. ie: available across many hosts in a decreased high availability for your apps.
This would mean if there is a top-of-rack failure etc, the VM’s on other racks are still available.
Any existing VM cannot be assigned to an availability set. Only when a VM is created, can we attach to an availability set. Existing VM if any will need to be deleted and created for the VM to put it into an availability set.
The two concepts in the Availaliablity set are
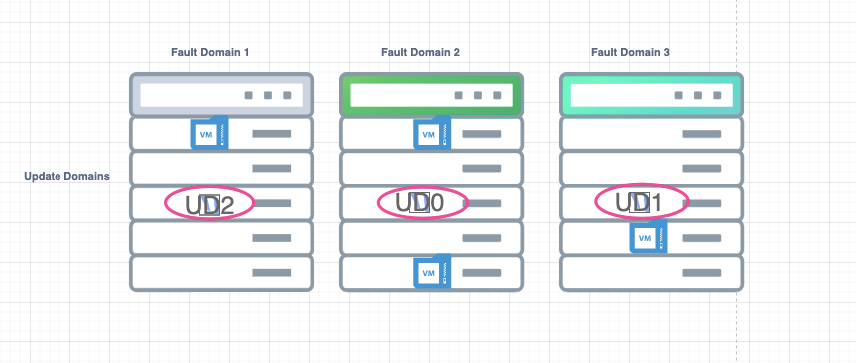
- Update Domains
- Fault Domains
Update Domains:-
During a planned maintenance window would Azure might be patching a host bios update etc that has all our VM’s which is why we use Update domains. They will do an update on the first one and then move on to the next. Each Update domain will be done separately to minimize downtime. Update domain 0 first and once done they move to the next one. During this process, we will need to shut or move VM’s on the host to peer hosts. Its recommended to have 5 update domains and this is because, our application should be running on at-least 4 virtual machines during an Azure maintenance period.

Fault domain – means rack awareness. If there was a TOR switch failure on the Fault domain 1 ( Rack 1 ) or a power feed issue on rack 1 just that VM’s on the rack will be affected. The peer racks ie: Fault domain 2 and Fault domain 3 aren’t affected
Availability set
The availability set allows spreading vm across multiple hosts in a dc. ie: available across many hosts in a dc. It’s thus a feature for managing the availability of our machines.
Create an Availability set and adding Servers to an Availability set
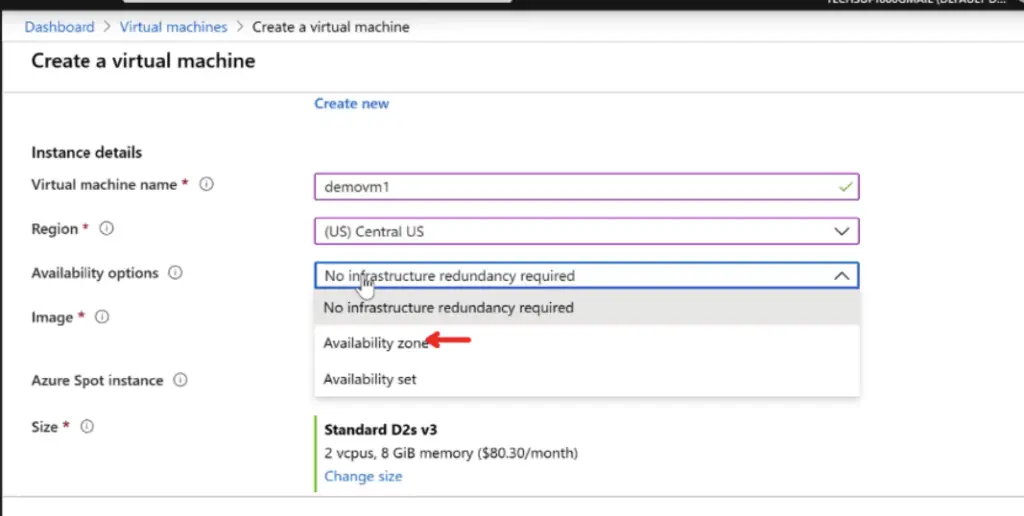
1 Create an Availability set

2 Create a virtual machine as usual and choose our availability set as the one we created

Adding a new VM to the Availability set.
Follow the same process as above.
Proximity Group
Proximity is just placing vm close for fast communication

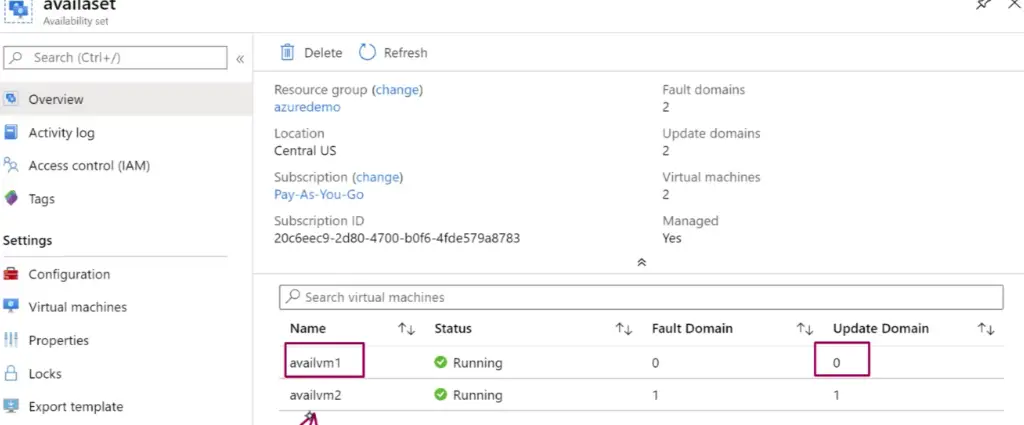
Our Fault and Update Domain will be shown

Placing a new virtual machine in the availability set
Below is a snapshot of what would happen if we placed another virtual machine in the availability set. The availability set service would place the machine accordingly so that the virtual machines get placed across the various fault and update domains.
Availability Zone (Datacenter level failure)
Each Availability Zone is a unique physical location in an Azure region ( eg: North Europe ). Each zone comprises one or more data centres that have independent power, cooling, networking etc. AZ is just a collection of data centres in a region that is physically separated and helps protect applications against data centre failures. There are data transfer charges for replicating data between availability zones.

An Availablity zone allows vm (app, DB etc ) to be spread across multiple data centres in the same region. If one data centre was to go down due to some environmental issues etc, our VM’s will be available on our peer data centre.
This shows our VM is only in 1 AZ


