When you roll out VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF), the architecture always starts with a management domain. From there, you can add one or more VI workload domains, each tailored with its own compute, storage, and networking resources. These workload domains are kept separate from the management layer, giving you a clean boundary for hosting applications and delivering cloud-like services inside your private datacenter.
I’ll demonstrate a single-rack deployment using VCF Operations
VCF workload domain vCenters cannot be in linked mode. The architecture enforces separation, and SDDC Manager is the tool that ties everything together. Each workload domain is meant to be a self-contained unit with its own vCenter instance, NSX Manager, and supporting infrastructure. This separation ensures that management boundaries are clear and workloads don’t bleed across domains.
If you need a consolidated view, you use SDDC Manager dashboards and APIs, not Enhanced Linked Mode.
In the vCenter UI, go to Global Inventory Lists → Hosts.
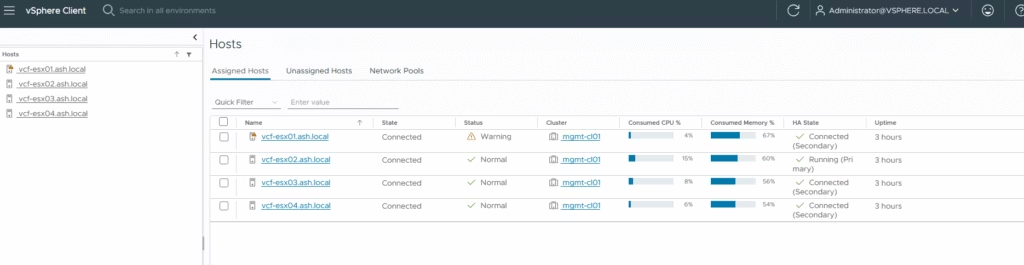
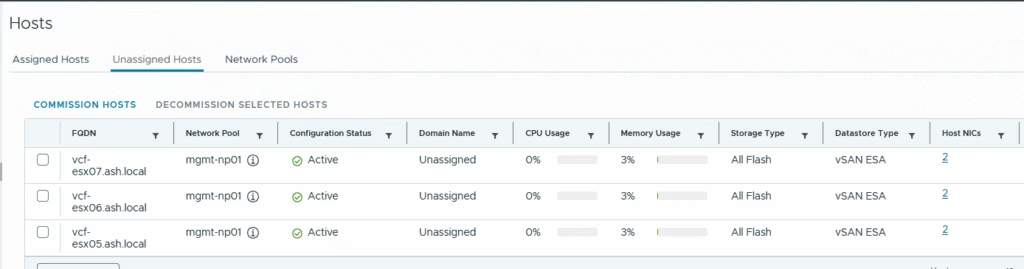
Switch to the Unassigned Hosts tab
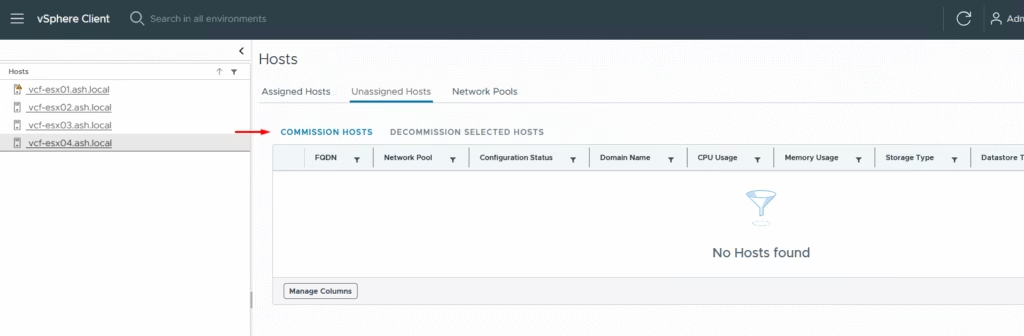
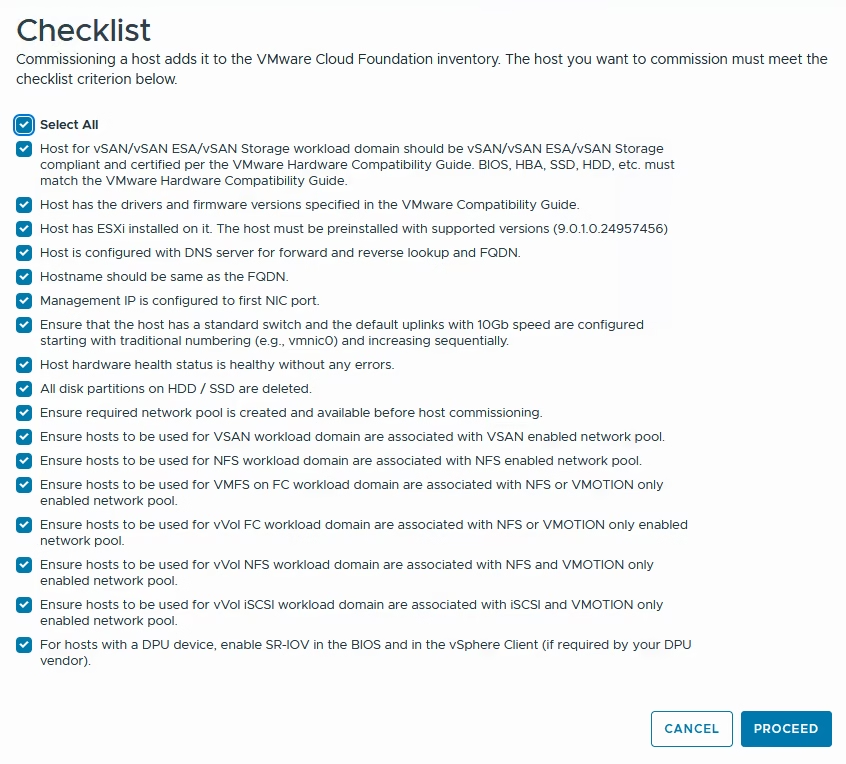
Click Commission Hosts
Once confirmed with checklist, click Proceed.
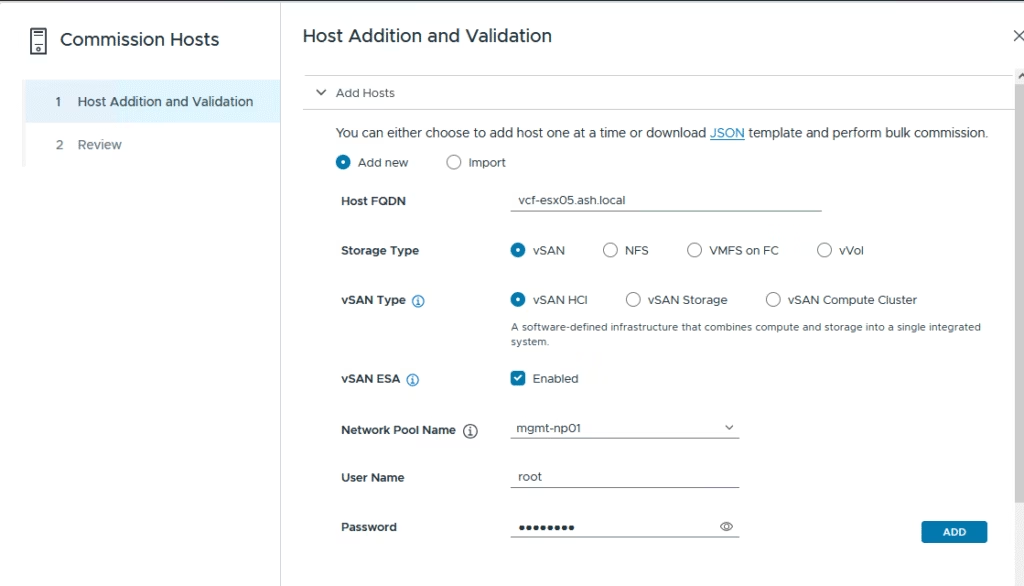
Add hosts one by one by entering the FQDN, storage type (e.g., vSAN), network pool, and root credentials.
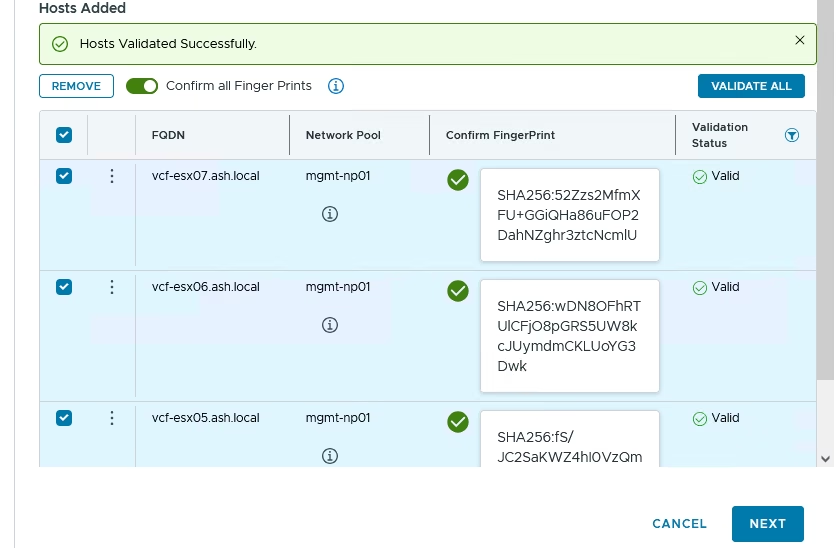
After adding hosts, click Confirm All Fingerprints to verify the SHA thumbprints
Click Commission to start the process.
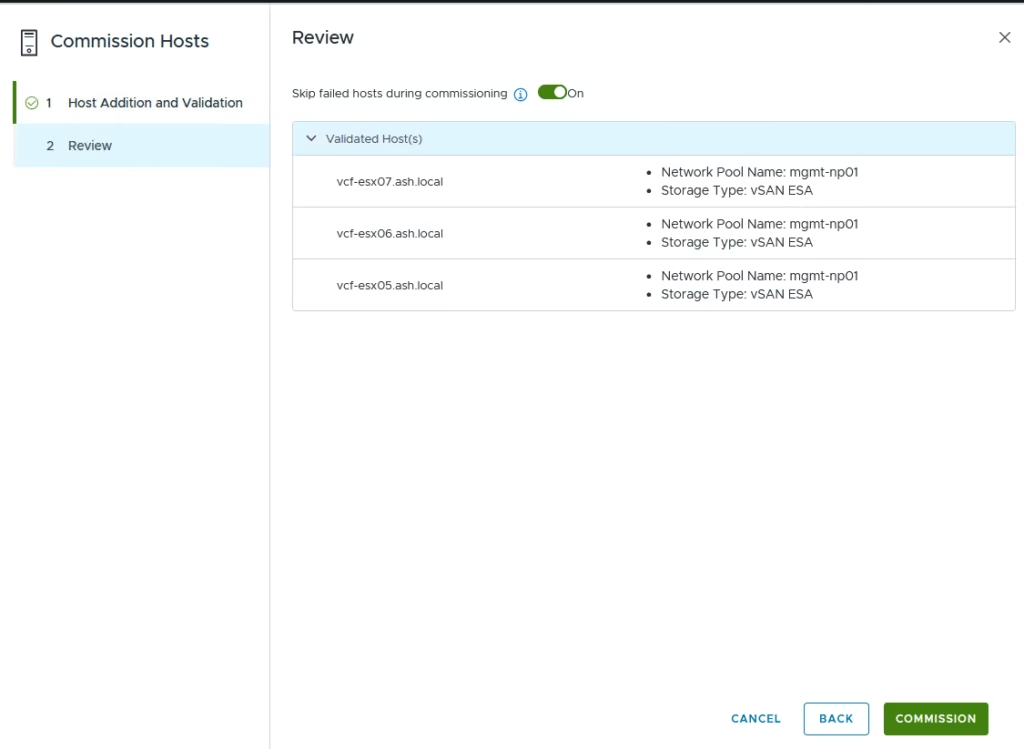
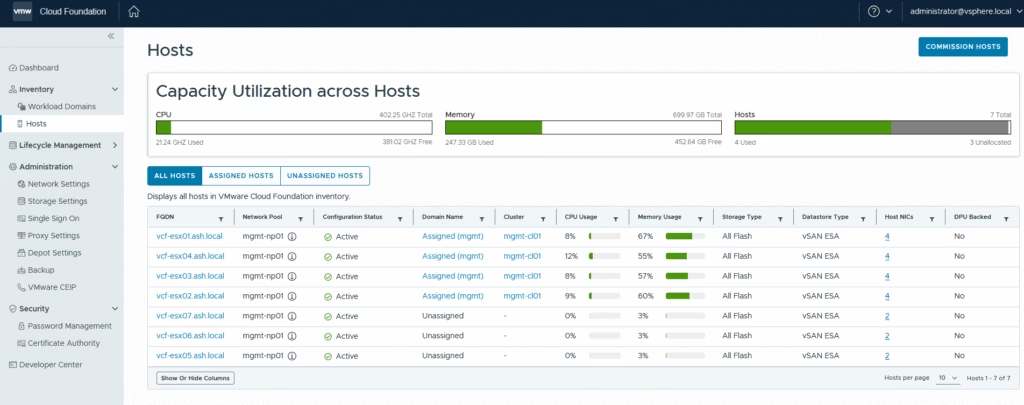
Once complete, the status changes to Active — meaning the hosts are ready to be used in workload domains or clusters.
Review it under the SDDC manager