If you have ever heard of AVI Networks, then it’s the same product. VMware purchased it and renamed it NSX AVI. This appliance is deployed as a standalone appliance and we will deploy several K8s architectures in our upcoming Kubernetes lab on vSphere.
What is AVI / ALB
Load balancing allows access to multiple servers using a single VIP address. Load balancer gives an equal distribution of load across the backend servers and also provides higher HA than using a single server.
AVI is an Active/Active software-based load balancer that can balance through the cloud, vCenter, Docker, Kubernetes etc and can scale very fast as per our deployment requirements.
AVI offers central management of all our load-balanced environments via a single pane of the window. Without AVI we will deploy a load balancer in every environment and then manage it individually just like Kemp load balancers, AWS ELB etc does.
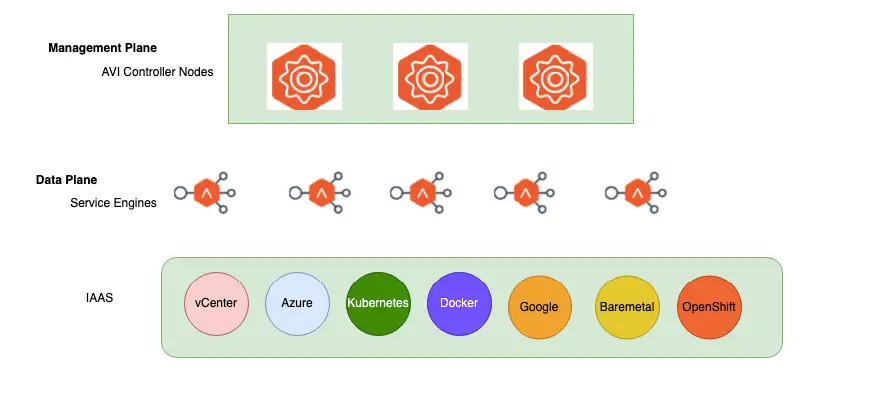
AVI Architecture
| Management | Controllers |
| Data Plane | Service Engine ( ie: Load Balancer ) |
AVI Components
ALB has the following components on it
- Controllers – Management Plane
- Service Engine – Data Plane
We only need to deploy the controller, while the SEs will be deployed automatically.
Controllers – Management Plane
The core component of AVI is the Controllers and it’s deployed as an OVA. AVI is deployed in a cluster of three for redundancy. If we lose 2 nodes, we can’t make any changes so AVI will just operate its last known configuration but will still pass traffic through it. The controllers are responsible for spinning up our service engines and holding the configuration data. Metrics from all service engines are sent to the controllers.
Service Engine – Data plane
Service Engine is actually the load balancer
Logical Components of AVI
Cloud – These are containers consisting of controllers, service engines and virtual services.
Virtual Services: IP addresses and ports for listening to client traffic.
Pools: Consists of server list and performs monitoring, load balancing etc. A list of server pools forms a pool group.
Health Monitor: This is used to monitor the server’s health eg: HTTP headers, TCP ping etc
Gateway monitoring: Health monitoring of the first hop gateway connected to the SEs is possible and uses ICMP echo.
AVI Deployment Types
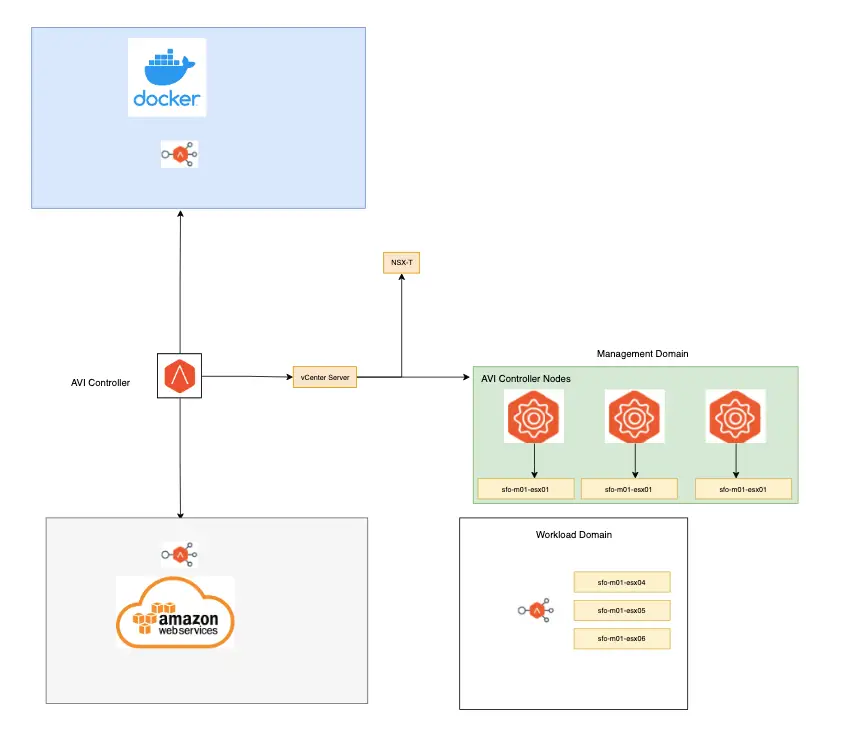
Applications in a hybrid cloud topology can be deployed anywhere and as well can be migrated quite easily, the advantage of AVI is the ability to deploy service engines under any infra and the ability for it to be managed via the same central UI.
AVI Licensing
The AVI lite version is included with the base NSX-T but it lacks analytics and has no Active/Active config. The controllers are free however the service engines need to be paid per CPU core.
| Deployment VM | CPU | Licensing Required |
| 4 SE | 1 vCPU | Require 4 AVI Service Core |
| 4 SE | 2 vCPU | Require 8 AVI Service Core |
AVI Lab Configuration
Prerequisites for NSX ALB Deployment:
- vSphere 7. X deployed and configured.
- NSX-T Manager deployed and configured – TO peered to TOR using BGP

