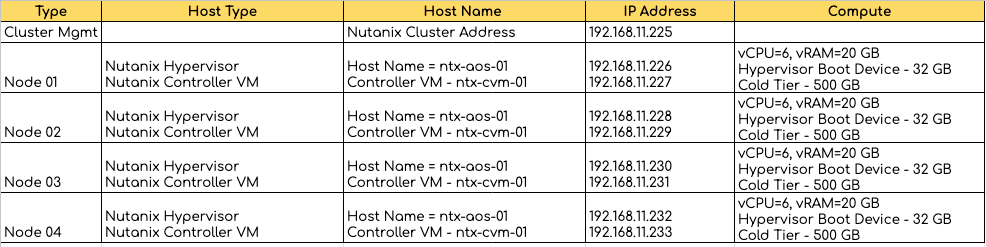
In this series, we will cover the deployment process of Nutanix Private Cloud Solution and how to configure HCI technology on a four-node cluster using the Nutanix Community Edition – a free version of Nutanix AOS (Acropolis operating system).
Nutanix CE is a free version of Nutanix AOS (Acropolis Operating System) that powers the Nutanix Enterprise Cloud Platform and can be used for testing all features of Nutanix. Nutanix HCI, like the vSAN virrtualiszes and moves local storage on
Nutanix Components
- Hypervisor – Acropolis hypervisor with virtualization management running Nutanix Acropolis OS
- Prism – A web console used to manage Nutanix cluster ie: the CV
- nCLI – The command line interface of Nutanix Environment.
- CVM – Cluster virtual machines
- Locality – This is one of the greatest features available on Nutanix. If a VM is created on a Host 1 for example, the CVM will place the disk of a VM on the local host itself so it means it’s all local. Behind the scenes, it’s all replicated to other hosts. Any request of data from the VM will go to the CVM which handles the i/o of the evnt. The CVM interacts with the vswtich , hba, and hard disk to get the data requested. So if the VM is on another host, CVM communicate to CVM on another host and gets data.
- AFS
- Acropolis OS
Comparing VMware EcoSystem and Nutanix
| VMware | Nutanix |
|---|---|
| ESXi | AHV |
| ESXi Host Client | PRISM Element |
| vCenter | PRISM Central |
| vSAN | AOS |
| vSAN Datastore | Distributed Storage Fabric |
| NSX | Flow |
| VMtools | Nutanix Guest Tools ( NGT ) |
Prerequisites for Nutanix Installation
- Register and download the Nutanix CE.
- Add DNS entries for all our 4 Nutanix hosts
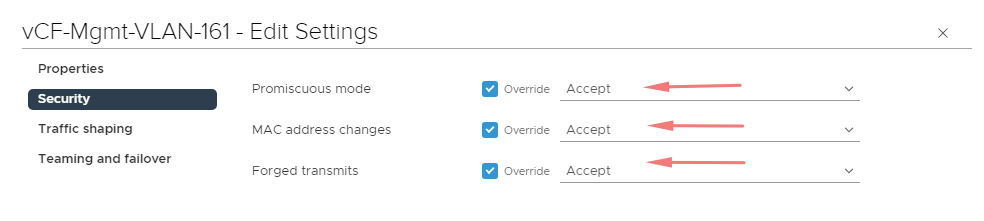
The portgroup should allow MAC address changes and Forget transmits
Creating the Nutanix CE VM
The community edition of Nutanix is free and can be installed on the below form factor on a nested VMware Lab cluster.
Open vCenter > Create a new virtual machine > Give the VM a name: (e.g. ntx-aos-01)
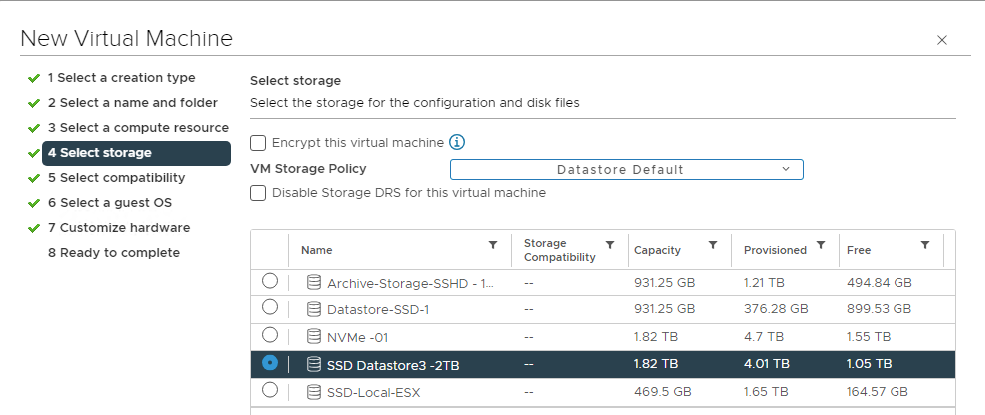
Choose the datastore as NVMe in our example
Select the compatibility level (e.g. ESXi 7.0 U2 and later)

Select the Linux / CentOS 7 (64-bit) guest OS
Spec the VM as per below config
- Change the CPU count to 4 and enable Expose hardware-assisted virtualization to the guest OS.
- Change the memory to at least 32 GB
- Reconfigure the New Hard disk: 16GB, Thin Provision as Hypervisor Boot disk.
- Add a second Hard disk – 200GB to serve as our Data disk.
- Add a third Hard disk – 500GB to serve as our CVM Boot disk.
- Set Network Adapter to VMXNet3
- VM Options > Boot Options > Firmware > BIOS
- Choose the management port group
- Mount the Nutanix CE ISO file to the VM
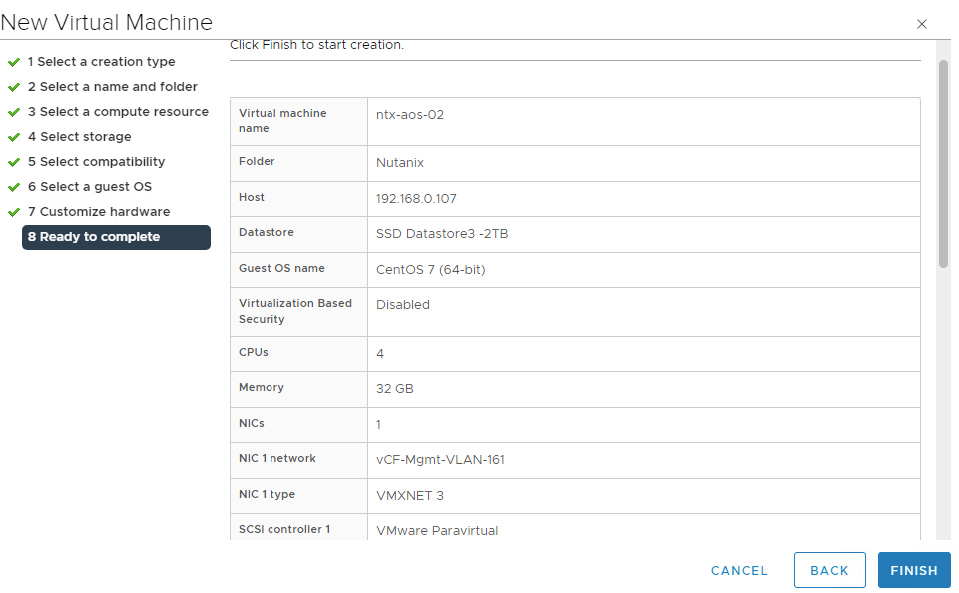
Validate all settings and Click Finish
Once the VM is powered on, we should see the screen below.
- H – Disk used for AHV
- D – Disk disk will be used for the Extent Store.
- C – Disk used for storing virtual machine disk data, CVM, OPLOG, and other service partitions.
A point to remember here is the installer will pick up the largest disk for CVM data but we can choose the CVM disk as we need by pressing the keys “ d”, “ c” and “ h” to move disks around.
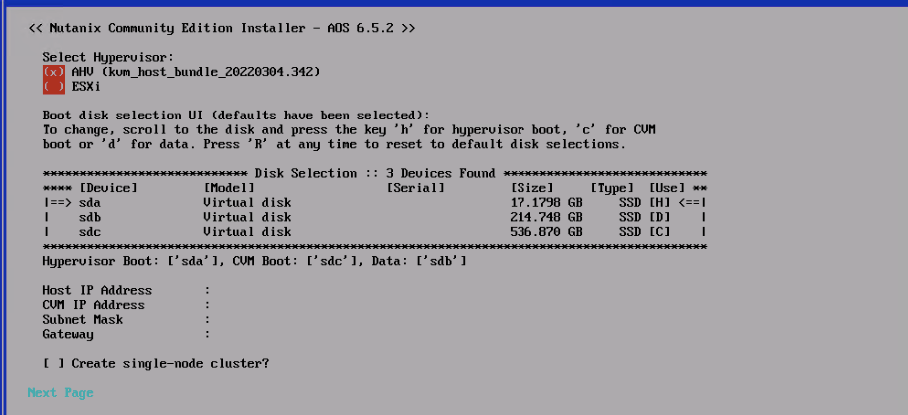
Enter the Host IP address, CVM IP address, subnet mask, dns and gateway. Check the single-node cluster box

Accept the EULA and click Start to begin the imaging process
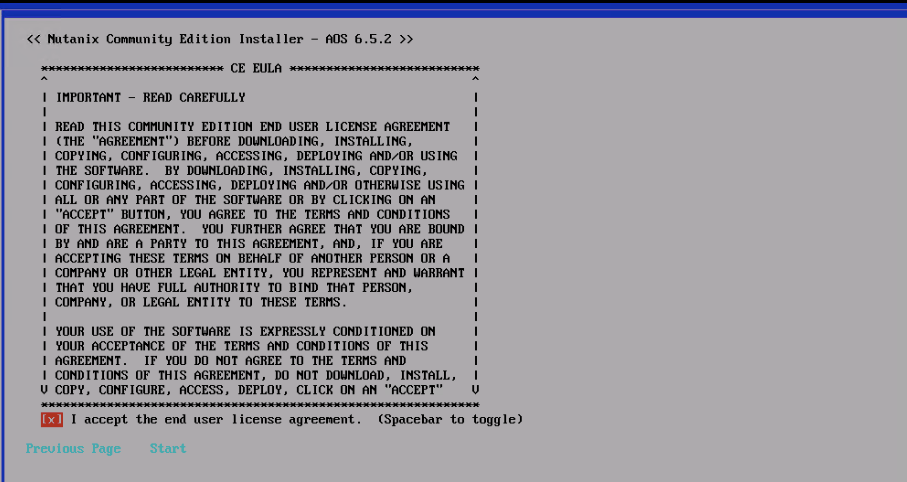
The imaging and deployment will take around 25 minutes our AHV will be ready and you will be asked to disconnect the ISO attached and reboot the system.
Once the hypervisor is rebooted, we will need the CVM virtual machine to be launched under AHV control which will take around 15 minutes to configure the CVM, create a cluster and start all cluster services.
Next, SSH to its CVM IP using the following credentials- nutanix/nutanix/4u

