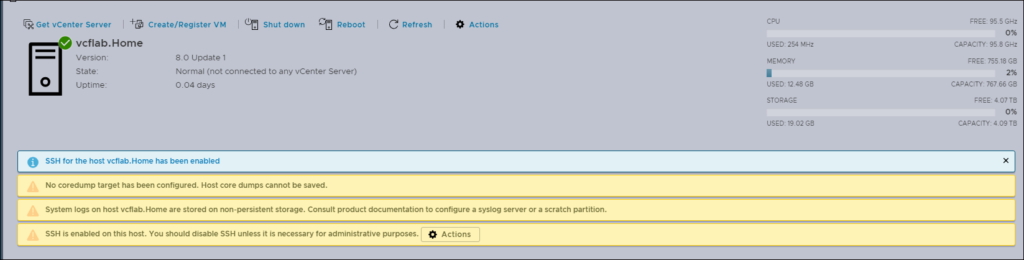
If you are using SD card or USB key for boot in vSphere 8, you may receive the warning below on ESX8.
What is Core Dump?
A core dump is diagnostic information being captured during a purple screen error or a host failure so this is the ROM data such as core dumps and configs. The core dump resides in a diagnostic partition which could either be on your UBS or a separate datastore.
Why Core Dump ≠ RAM Size
ESXi auto-sizes the core dump file based on kernel memory, not total RAM.
Core dump files don’t need to match your host’s total RAM because they only capture the ESXi kernel and system-level memory—not the memory used by your virtual machines. Even if your host has 700 GB of RAM and dozens of VMs, the dump file won’t include any of that guest memory. VMware’s auto-sizing logic is designed to estimate how much space is needed to capture the kernel state, which usually falls somewhere between 2 and 8 GB depending on the host’s configuration.
If you manually set the dump file size to match total RAM, you’ll end up wasting datastore space, slowing down the dump process, and complicating backup and retention. That’s why most admins either let ESXi auto-size the file or set a fixed size like 8GB that’s large enough to cover the kernel footprint but not excessive.
Coredump partition limitations
- It cannot be created on an iSCSI LUN (Both hardware and software) and No FCoE LUN.
- Diagnostic partitions cannot be create using vCLI however the existing partitions can be activated.

First two default values can be changed under the Settings of VMware vSphere ESXi Dump Collector Service. More customization can be done by editing the configuration file which will be discussed below.
To view the core dump partition from your ESXi host execute below command from the ESXi CLI.
esxcli system coredump partition list
root@vcflab:/vmfs/volumes] esxcli system coredump file add -d SmallDatastore -f vcflab-host01
[root@vcflab:/vmfs/volumes]
[root@vcflab:/vmfs/volumes] esxcli system coredump file set -p /vmfs/volumes/SmallDatastore/vmkdump/vcflab-host01.dumpfi
le
[root@vcflab:/vmfs/volumes]
[root@vcflab:/vmfs/volumes] esxcli system coredump file list
Path Active Configured Size
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------ ---------- ----------
/vmfs/volumes/66a47473-bf0a786a-9bbf-d06726cd0b96/vmkdump/vcflab-host01.dumpfile true true 8767143936
[root@vcflab:/vmfs/volumes]
[root@vcflab:/vmfs/volumes] esxcli system coredump network check
Network coredump not enabledYou can check the dump configuration via ESXi Shell or SSH:
esxcli system coredump file list
esxcli system coredump network get
esxcli system coredump partition getYou can reconfig the dump configuration via ESXi Shell or SSH:
# 1. Disable the current core dump file
esxcli system coredump file set --enable false
# 2. Remove the existing core dump file
esxcli system coredump file remove --force
# 3. Create a new dump file named after the host, with fixed size
esxcli system coredump file add --datastore=YourDatastoreName --file=$(hostname -s).dump --size=8585216
# 4. Enable the new dump file
esxcli system coredump file set --enable true
# 5. Verify the configuration
esxcli system coredump file list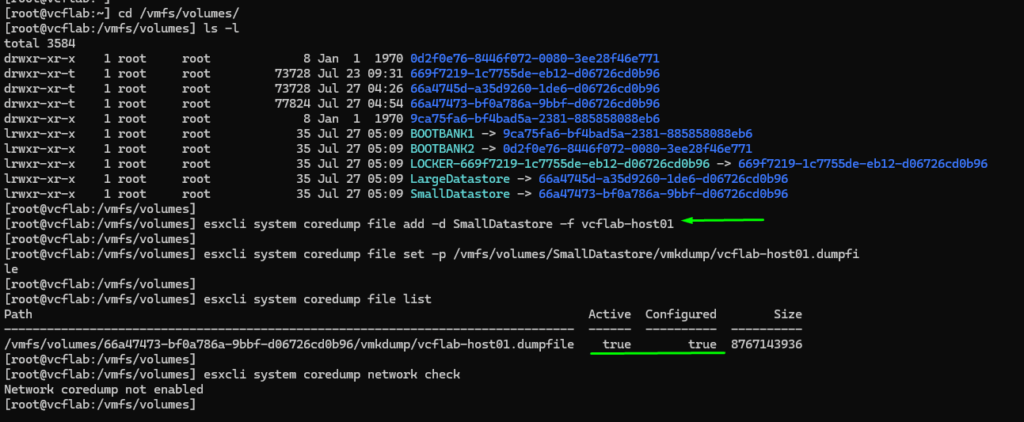
Common Causes of Core Dumps
- Faulty hardware (RAM, CPU, NICs, HBAs)
- Buggy driver or firmware
- Incompatible third-party modules

