Minikube is a lightweight Kubernetes clusters cluster for labs, demos, and automation development. It runs locally, uses Docker as the container runtime, and gives you a full Kubernetes API without the overhead of a multi‑node cluster.
This guide focuses only on installing and configuring Minikube on Ubuntu
Prepare Ubuntu Server

Use the latest Ubuntu Server image and Install open-vm-tools and open ssh
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y open-vm-tools && sudo reboot
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y openssh-server && sudo systemctl enable --now ssh
🐳Install Docker (Required for Minikube Driver)

Deploy docker from https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/#install-using-the-repository
Add Docker’s official GPG key:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ca-certificates curl
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
Add Docker repository
# Add the repository to Apt sources:
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.sources <<EOF
Types: deb
URIs: https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu
Suites: $(. /etc/os-release && echo "${UBUNTU_CODENAME:-$VERSION_CODENAME}")
Components: stable
Signed-By: /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
EOFInstall Docker Engine
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-pluginTo verify that Docker is running, use:
sudo systemctl status dockerAdd your user to the Docker group for sudo
awxadmin@awx:~$ echo $USER
wxadmin@awx:~$ sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
#update user without logout
awxadmin@awx:~$ newgrp docker
Install and Configure Minikube Cluster on Ubuntu

Minikube is open source tool used to run a single node kubenertes cluster on a system for testing
Install Minikube Dependencies
sudo apt install -y curl wget apt-transport-httpsDownload and Install Minikube Binary
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64
sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikubeVerify Minikube Installation
minikube versionInstall kubectl

kubectl is the command used to interact with kubernetes cluster
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
Set executable permission and move kubetcl to /usr/local/bin/
chmod +x kubectl
sudo mv kubectl /usr/local/bin/
Verify kubectl version
awk@ansible:~$ kubectl version -o yaml
clientVersion:
buildDate: "2024-08-13T07:37:34Z"
compiler: gc
gitCommit: 9edcffcde5595e8a5b1a35f88c421764e575afce
gitTreeState: clean
gitVersion: v1.31.0
goVersion: go1.22.5
major: "1"
minor: "31"
platform: linux/amd64
kustomizeVersion: v5.4.2Start Minikube Cluster
Minikube defaults to 3GB RAM and 2 CPUs. For most automation labs, this is fine — but you can scale it later
Start with Docker driver
minikube start --driver=dockerYou should see output similar to:
awk@ansible:~$ minikube start --driver=docker
* minikube v1.38.0 on Ubuntu 24.04
* Using the docker driver based on user configuration
! Starting v1.39.0, minikube will default to "containerd" container runtime. See #21973 for more info.
* Using Docker driver with root privileges
* Starting "minikube" primary control-plane node in "minikube" cluster
* Pulling base image v0.0.49 ...
* Downloading Kubernetes v1.35.0 preload ...
> preloaded-images-k8s-v18-v1...: 271.45 MiB / 271.45 MiB 100.00% 1.78 Mi
> gcr.io/k8s-minikube/kicbase...: 514.15 MiB / 514.16 MiB 100.00% 2.24 Mi
* Creating docker container (CPUs=2, Memory=3072MB) ...
* Preparing Kubernetes v1.35.0 on Docker 29.2.0 ...
* Configuring bridge CNI (Container Networking Interface) ...
* Verifying Kubernetes components...
- Using image gcr.io/k8s-minikube/storage-provisioner:v5
* Enabled addons: storage-provisioner, default-storageclass
! /usr/local/bin/kubectl is version 1.31.0, which may have incompatibilities with Kubernetes 1.35.0.
- Want kubectl v1.35.0? Try 'minikube kubectl -- get pods -A'
* Done! kubectl is now configured to use "minikube" cluster and "default" namespace by default
awk@ansible:~$This confirms Minikube is configured and running with Docker.
awk@ansible:~$ minikube status
minikube
type: Control Plane
host: Running
kubelet: Running
apiserver: Running
kubeconfig: ConfiguredRun free-m & docker stats can be used to see the memory assigned so here is a 3GB limit which needs to be changed

Adjusting Minikube Resources (Optional)
awk@ansible:~$ minikube delete
Deleting "minikube" in docker …
Deleting container "minikube" …
Removing /home/awk/.minikube/machines/minikube …
Removed all traces of the "minikube" cluster.
awk@ansible:~$
awk@ansible:~$Start with custom resources
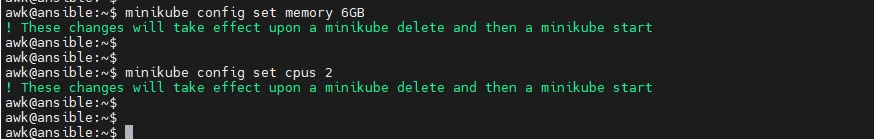
Start minikube creates docker container with 6 GB memory
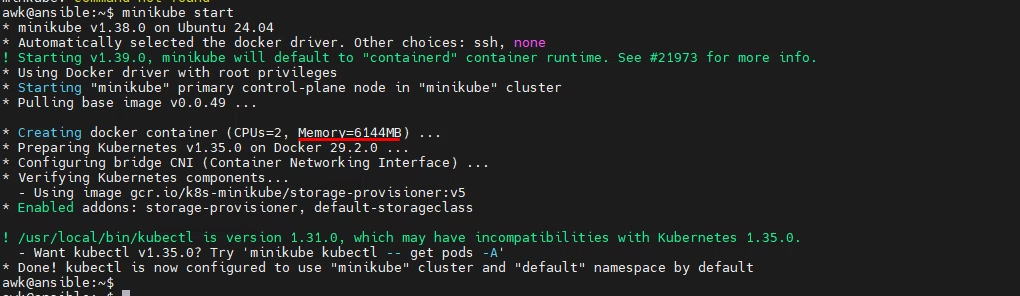
Verify with Docker
docker stats
Verify Kubernetes Nodes
wk@ansible:~$ kubectl get nodes
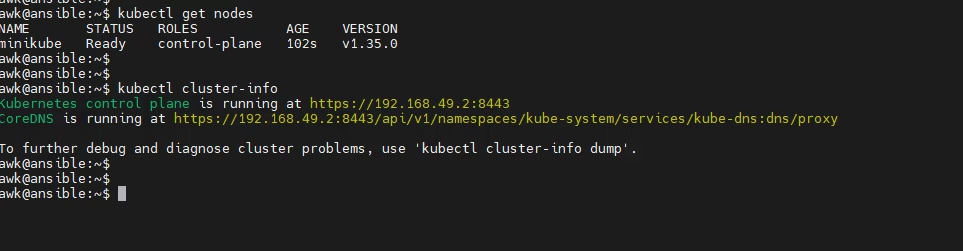
Verify Kubernetes Cluster info
awk@ansible:~$ kubectl cluster-info
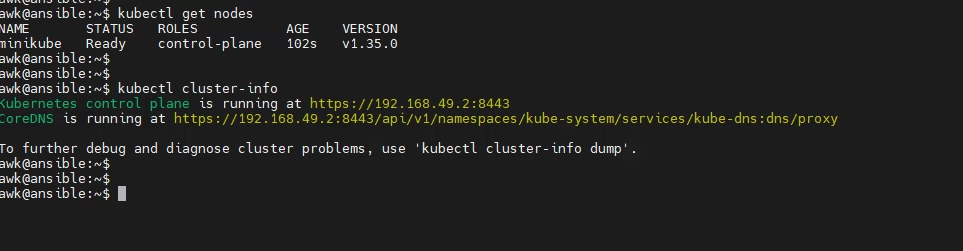
Shows pods
awk@ansible:~$ kubectl get pods -A
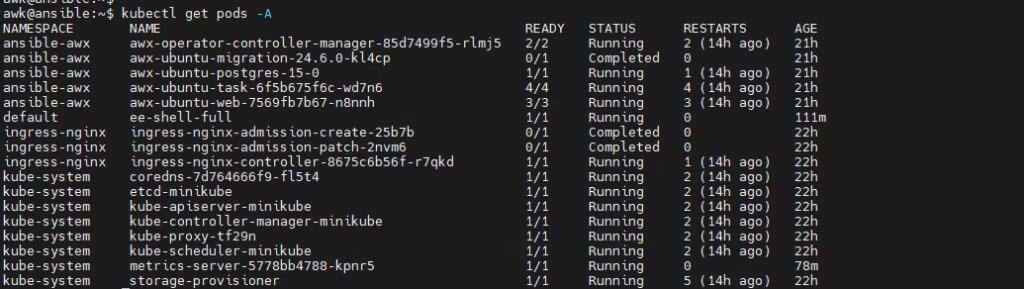
Shows pods only in the current namespace.
awk@ansible:~$ kubectl get pods