In this blog, we will take a look at how to enable vSAN in a vCenter cluster. We’ve covered the deployment of vSAN 2-node cluster in our earlier topic, and using of a witness host to enable the functionality – the stretched cluster works just the same but uses a special Witness OVA file that needs to be downloaded and deployed.
Blog Series
- Configure vSAN in Single Site
- Create vSAN SSD Disks from HDD
- Remove an esx node from the vSAN cluster
- Scaling vSAN by adding a new esx node
- Two nodes vSAN7 Configuration
- Convert 2-Node vSAN to 3-node configuration
- VMware vSAN Stretched Cluster
Introduction to Stretched Clusters
This would be familiar to some people as this is the same old EMC VPLEX configuration that needed expensive block-based arrays. Back in the day, we used EMC VPlex to deliver Active/Active mirrored disk configurations ( RAID 1) but this can now be done via the vSAN stretched cluster fully via a software-based solution. Data thus within the stretched cluster are evenly spread across (mirrored) and joined by a high bandwidth network providing data resiliency across sites. From a management point, its still a single vSAN datastore. HCI mesh is not supported on stretched clusters.

ESX hosts within the stretched cluster configuration have their data just spread around all between the members using a concept called fault domains – (a boundary of failure) using DRS rules. In the event there is an outage on the primary site, it will not have an impact as the replica disks will be served via the secondary site very similar to the standard vSAN architecture.
Components of a vSAN Stretched Cluster
The brain behind the formation of a vSAN cluster lies in a special purpose VM called witness VM or witness host. This is a special-purpose OVF file that looks similar to our ESXi version and it’s downloaded separately from the VMware portal.
This witness VM acts as a tie-breaker or a quorum disk to maintain the metadata between members participating in the fault domain. This concept of a quorum is very similar to the IBM SVC Storage SAN Controller quorum- topology.
We will have a primary site with a minimum of 3 ESXI hosts and a secondary site with an equal number of ESXI hosts. All we are doing in the stretched cluster is grouping these sites together via a low latency and high bandwidth link by creating a fault domain.
One fault domain thus is a primary site + secondary site + the witness host.

Prerequisites of a vSAN Stretched Cluster
A vSAN Enterprise license is required for vSAN Stretched cluster.
Refer Stretched Cluster Bandwidth Sizing Guide
Witness to Sites
- Network latency between the witness and sites should be under 200ms
- The network connection between the sites and the witness should be configured as L3
Sites to Sites
- 10 GB bandwidth between site 1 to site 2 and a round trip time be under 5ms
- Configure the network (vlan) between sites within the Layer 2 boundary so we don’t need to RE-IP again post the HA failure
Deploy the Network PortGroups for Witness vSAN Appliance
The vSAN Witness Appliance contains two network adapters. The first network witnessPG VMkernel interface (vmk1) is used to communicate with the vSAN Network and the second one will connect to our vCenter management ( vmk0).
The vSAN Witness Appliance Management VMkernel is attached to one VSS, and the WitnessPG is attached to the other VSS. The Management VMkernel (vmk0) is used to communicate with the vCenter Server for appliance management. The WitnessPG VMkernel interface (vmk1) is used to communicate with the vSAN Network. This is the recommended configuration.
I’ve gone ahead and deployed it all under one vSwitch and under one vmkernel adapter for this lab

As shown all necessary services are enabled under one vmkernel adapter

Deploy VMWare VSAN Witness Appliance
We will first need to deploy a vSAN Witness Appliance. Unlike how we configured, the witness in our 2-Node vSAN config stretched cluster needs a special Witness OVA file that needs to be downloaded and deployed.
1- Log in to the VMware portal and download the VMware VSAN witness virtual appliance.

2-Deployment of the VSAN witness appliance just as easy as deploying any other OVA file on the vCenter

3-Review details and click proceed to continue

4- Accept all license aggrements

5- Choose the deployment size needed. The size of the witness VM depends on the expected number of VMs in the VSAN stretched cluster
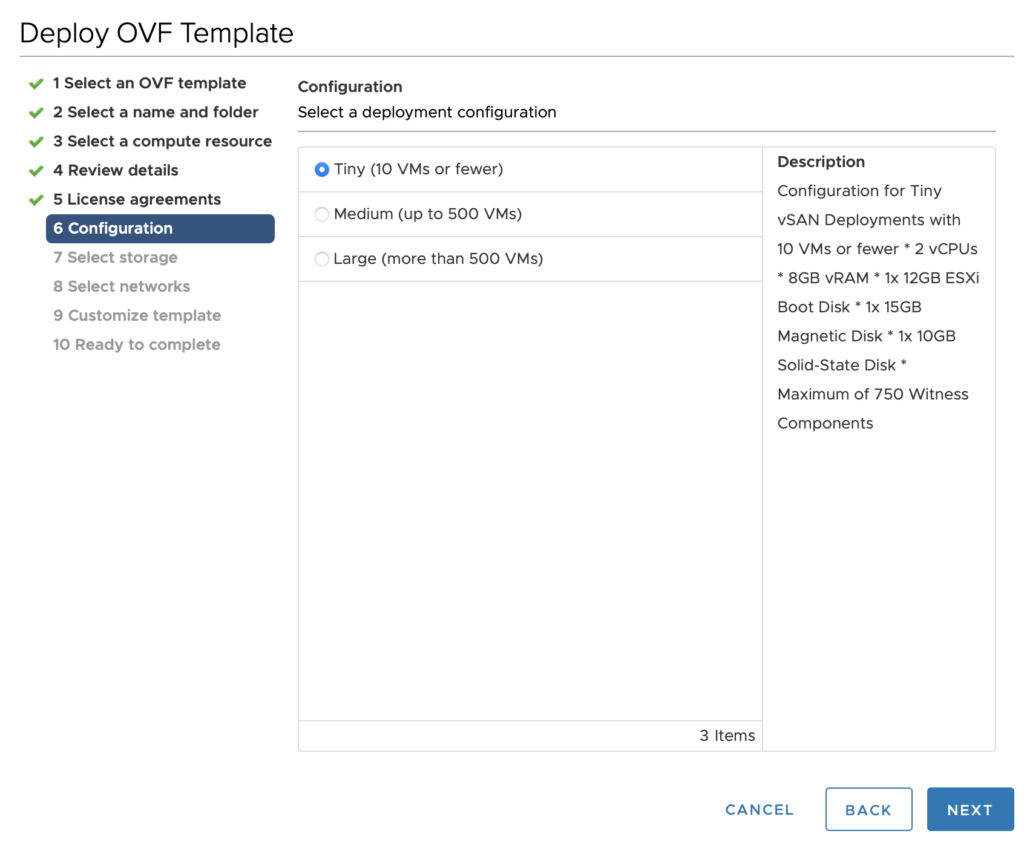
6- Choose the datastore location to deploy the VM to

7- Choose the Witness network as vsan-witness and management as Mgmt-1611 portgroup we defined earlier

8- Add a root password

9- Choose finish and power on the VM

Add Witness Host to vCenter Server
In this section, we will add our Witness host to our vCenter inventory. This is a plain VM running on another cluster somewhere.
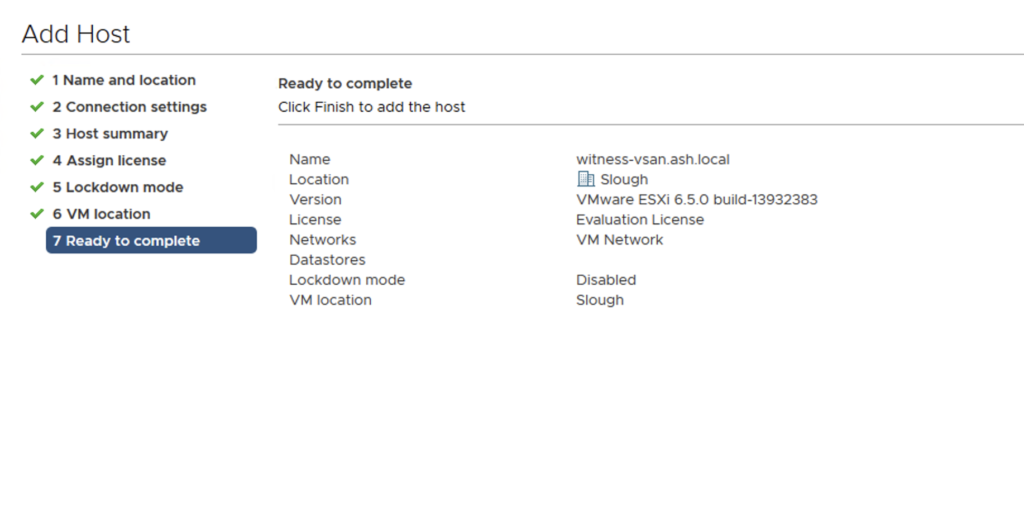
10- Choose to Add the host to the vCenter inventory.

11- Review all details and Click Finish
12- As you can see below, the witness host shows up as a BLUE ESXi host on our vCenter inventory

Configure VMware vSAN 7 Stretched Cluster
13- We have now 6 ESXI hosts in the cluster

14- Under Cluster – Configure vSAN – Choose the option Stretched Cluster

15- If our vSAN network is enabled on all hosts we should see Green

16- Claim Disks mapped to the host into Cache and capacity tier

17- We will move 3 hosts into the secondary fault domain and place 3 of hosts in primary fault domain

18– It will now ask you to point to the Witness Host we created earlier

19- Claim Disks mapped to the host into Cache and capacity tier

20- Review and finish configuration

21- Our Stretched cluster is enabled as shown and our ESXI is correctly in its fault domains

Configure Dual Site Mirroring for vSAN Stretched Cluster
22- With the stretched cluster thus created, we can now turn on our dual-site mirroring for our vSAN cluster and this happens under the VM Storage Policies.

23- Edit the default vSAN Storage Policy – Change the Site disaster tolerance to Dual site mirroring ( Stretched Cluster ).

24- Our vSAN storage will be displayed

25- Review and Click Finish

26- Now, we have a stretched cluster that is configured for dual-site mirroring a copy of the data should go to both sites, and the witness component should be placed on the vSAN witness host as shown

With a VM installed in our Site1, a copy of that VM is also placed in Site 2, and a witness keeps track of the VM. Whenever there is an outage scenario on our first data site, based on the voting algorithm, the vSphere HA will bring up the VM in the peer site.
Introduction to vSAN+ and vSphere+
This is the latest VMware offering which is a subscription-based licensing model that extends the VMware cloud vSAN to on-prem workloads to offer centralized management of our hybrid vCenter. A VMware Cloud gateway virtual appliance is spun up and once connected we will have everything managed via a single UI.
Conclusion
We have covered the very core feature of vSAN in this topic. In the next section, we will cover upgrading the vSAN cluster.

