A container image is an all-packaged configuration that includes source code, its dependencies and libraries that are needed to deploy applications in a container. We can pull base images from the central repository known as Docker Hub.
Container Workflow
A container workflow involves processes like
- Building an image
- Sending an image to the image registry
- Download an image from the image registry
- Finally, run the image as a container.
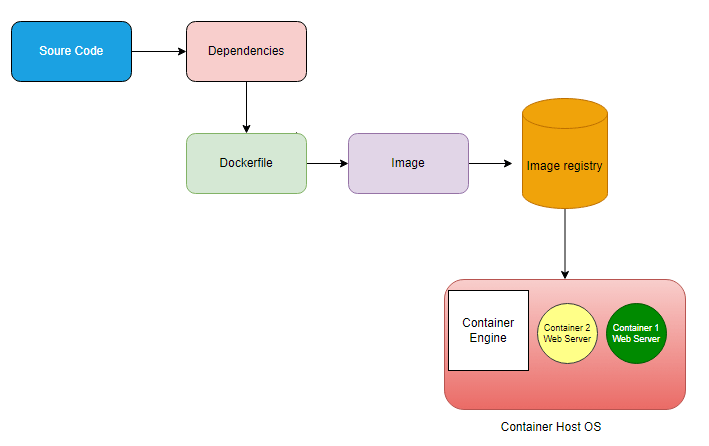
Image Registry is a central location where all the container images are stored so this will be Docker Hub.
# To search for an official image in docker hub
docker search xwiki –filter is-official=true
docker search <imagename>
docker search image –limit 5
# To download a new image:
docker pull centos:latest
# Show all documentation of images
docker image –help
# To show all image:
docker image ls
# # stop all running containers
docker stop $(docker ps -q)
# remove all containers
docker rm $(docker ps -aq)
# remove all image
docker rmi $(docker images -q)
# To assign a TAG to an image
docker tag imageid tag1:tag2
# To add another tag to an existing image with a tag
docker tag imageiD existingtag:v1 newtag:v2
# To “delete” an image: ( ie: remove image downloaded )
docker rmi image
# To remove all untagged images
docker image prune
# To remove images with no containers connected
docker image prune -a
# To remove all untagged images:
docker rmi $(docker images | grep “^<none>” | awk “{print $3}”

