vSAN abstracts and aggregates locally attached disks in a vSphere cluster to create a storage solution that can be provisioned and managed from vCenter. vSAN 8 with vSAN Express Storage Architecture, uses NVMe-based TLC flash devices rather than the traditional flash devices used to build a hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI)
vSAN can be deployed either as an OSA model or an ESA model.
Deployment models of vSAN8
- vSAN Original Storage Architecture (OSA)
- vSAN Express Storage Architecture (ESA)
vSAN Original Storage Architecture (OSA)
The classic storage architecture is the one with a dedicated cache and capacity drives available as a hybrid ( HDD+Flash ) or an all-flash configuration configured as disk groups. The same old concept of a dedicated cache tier that had to be allocated with the remainder of the disk configuration being configured for capacity or actual storage of our VM files is what the OSA provides. Existing clusters running on vSAN OSA models can be migrated to OSA vSAN 8.

vSAN Express Storage Architecture (ESA)
This one is optimized for purely NVMe drives, gets rid of the disk group configuration and uses storage pools. In the ESA model, all the devices in the pool contribute to the performance and capacity which is a massive improvement in storage utilization and performance as a whole.

Some of the Advantages of vSAN 8 -ESA over vSAN OSA
vSAN 8 ESA has some great advantages over the OSA model.
- Improved health and what-if analysis to show cluster capacity
- Replaces Cache disks and Disk groups with Storage Pools so that itself is a huge storage improvement.
- ESA offers improved CPU efficiency, improved availability with reduced failure domains, simplified storage device provisioning with proactive insights, and RAID-6 data storage with RAID-1 performance.
- Lower CPU usage per processed IO
- Highly Efficient Data Compression and encryption
- Snapshots with minimal performance impact
- Proactive notifications for environments not enrolled in the Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP) are available in both vSAN OSA and ESA deployments and this is quite handy for Limited Connectivity Environments that need health monitoring
- vSAN 8 has improved cache device size for the OSA model
- Designed and Optimized for NVMe-based storage devices
- Offers High Performance over the OSA model
Prerequisites for vSAN8 ESA
- vSAN 8 needs certified hardware to run – ESA-ready nodes.
- 4 NVMe disk devices per host to a max of 24 drives per node.
- vSAN ESA requires advanced or enterprise licenses.
- No direct upgrade path from traditional vSAN OSA to ESA. VMs need to be migrated to ESA via sVMotion/vMotion. ESA and OSA clusters can coexist in the same vCenter.
- 25GB Network Connectivity
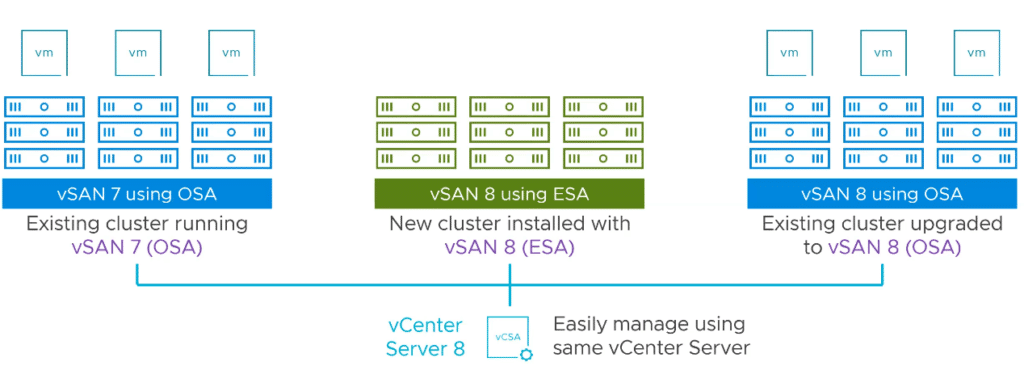
Migrating Path to vSAN ESA
There is no direct upgrade path from vSAN 7 OSA to vSAN 8 Express Storage Architecture. VMware vSAN 7 (vSphere 7) can be upgraded in place to vSAN 8 (vSphere 8) with the original storage architecture (OSA).
- Stand up your new vSAN ESA Cluster.
- Apply vSAN Advanced or Enterprise Licensing
- Migrate your Virtual Machines with Storage vMotion without any downtime
- ESA and OSA clusters can coexist in the same vCenter.
Configuring a vSAN 8 ESA
We have 4 ESXi hosts deployed in our environment and I’ve placed all the hosts in maintenance mode ready to be joined to the Cluster
| vCenter | 8.1 |
| vcf101 | 8.1 |
| vcf102 | 8.1 |
| vcf103 | 8.1 |
| vcf104 | 8.1 |
| vcf105 | 8.1 |
We’ve now deployed ESXi 8.1 on all our ESXi hosts and have vCenter is now on 8.1. Hosts are connected to a distributed switch with vDS v8.0 with MTU 9000 across.

Prerequisites for vSAN
- Hosts running on ESX 8. X and vCenter are on 8. X
- All 25GB vnic’s should be attached to vDS
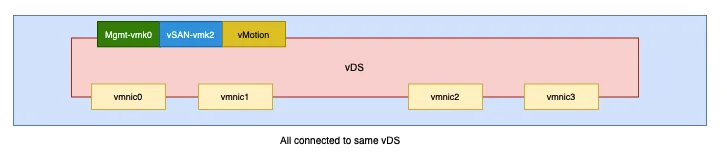
The current config is as below and we will make some changes to this to configure to our used case.
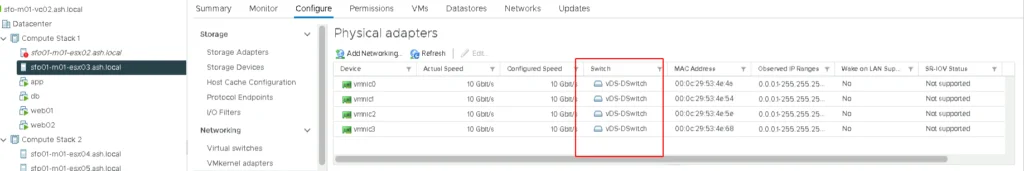
Network Config- Teaming & Failover
On the distributed switch, vmnic 3 and vmnic4 will be used for data traffic and vmnic1 and vmnic2 will be used for management traffic.
| Adapters | Use | Uplink |
| VMNIC0 | Active – Mgmt+vSAN+vMotion | vmnic0 |
| VMNIC1 | Standby – Mgmt+vSAN+vMotion | vmnic1 |
| VMNIC2 | left for NSX ( data traffic ) | vmnic2 |
| VMNIC3 | left for NSX ( data traffic ) | vmnic3 |
Our configuration for Mgmt vmk will be
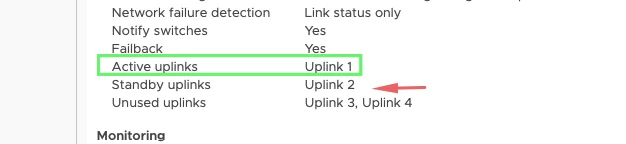
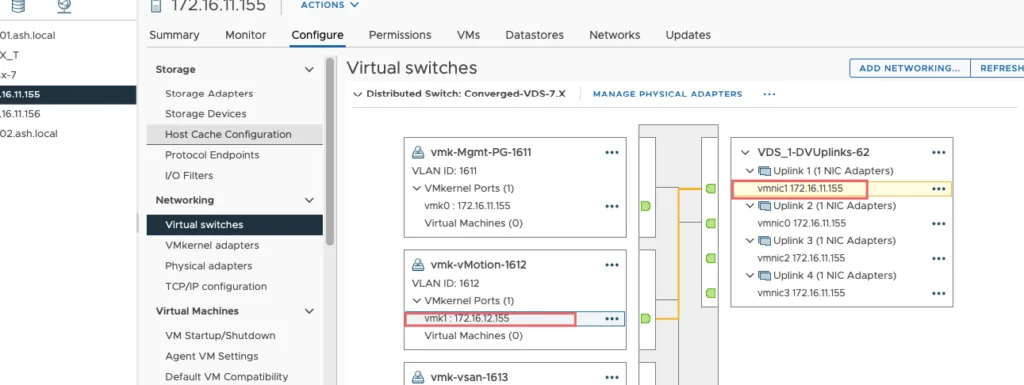
Our configuration for VMotion vmk will be

For vSAN vmk, will use uplink 2 (vmnic2) as the active interface because we need dedicated bandwidth for vSAN so just a reverse of what’s on mgmt and vSAN VMkernel.
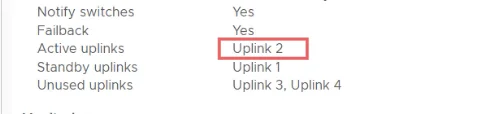
Mgmt- vDS Config
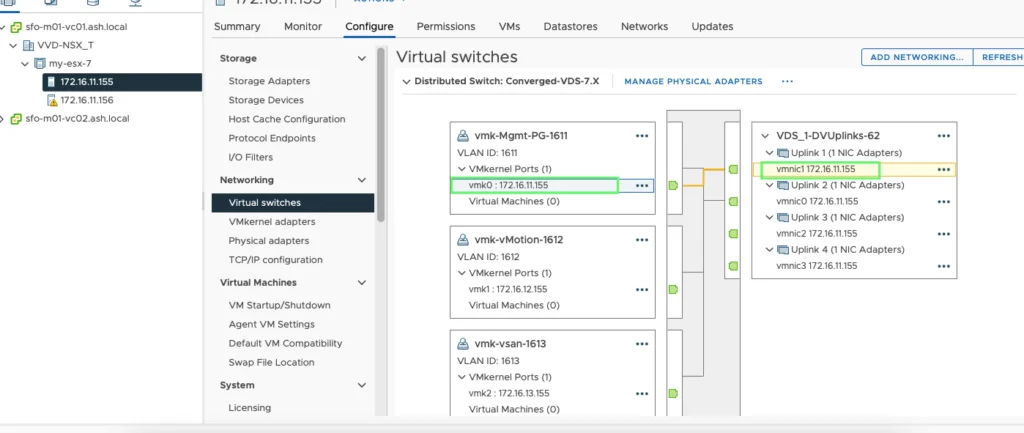
vMotion – vDS Config
vSAN – vDS Config

Creating a vSAN ESA Cluster
1. Login with VMware vSphere client, Select Datacenter, select the Menu tab and then click on New Cluster.
2. At the time of VSAN cluster creation, enable the vSphere HA, vSphere DRS features and choose the option to manage all hosts with a single image
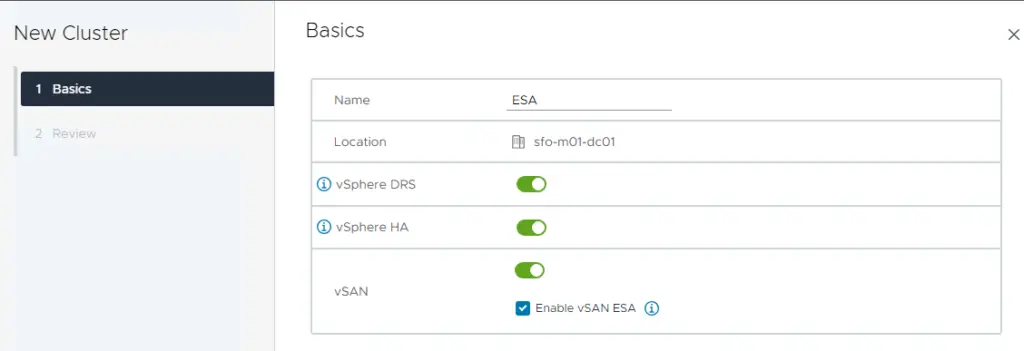
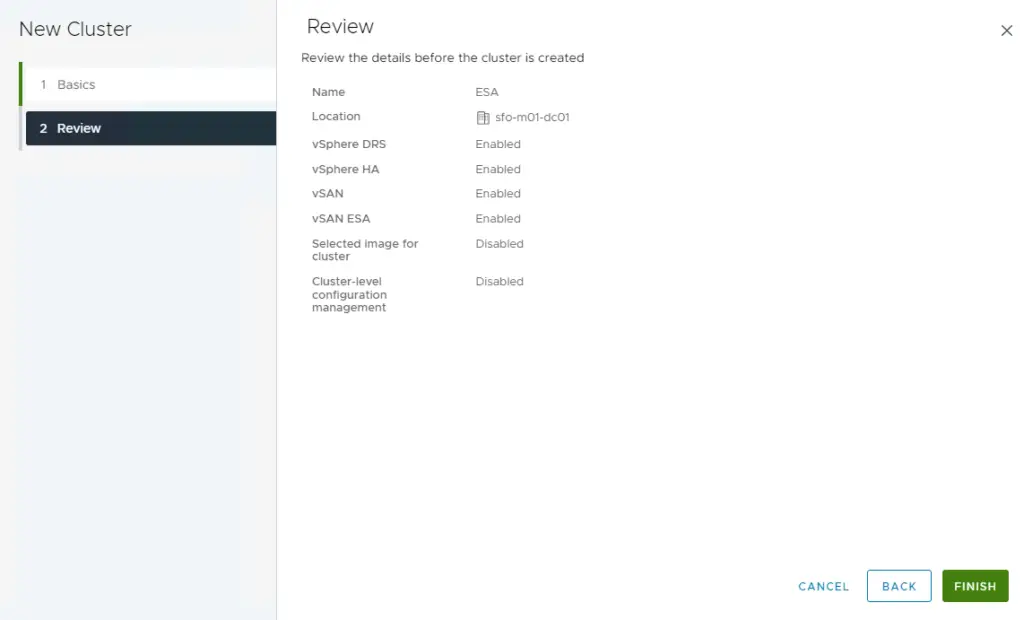
3. Review and click finish
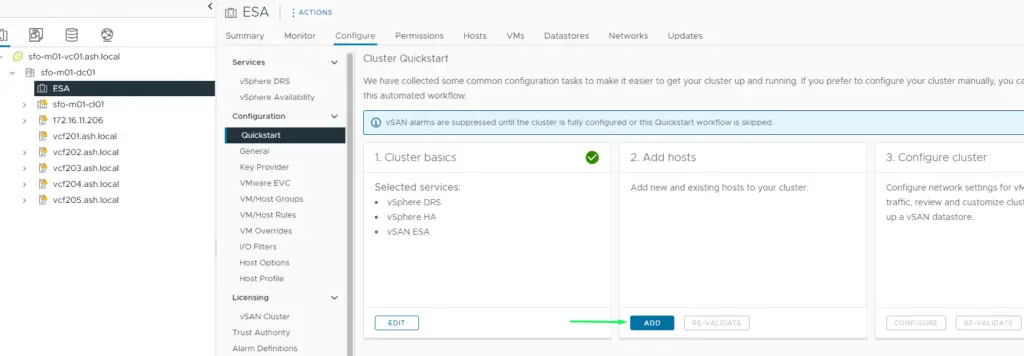
4. To turn on vSAN, select the Cluster – Navigate to Configure tab – vSAN Services and Click Configure
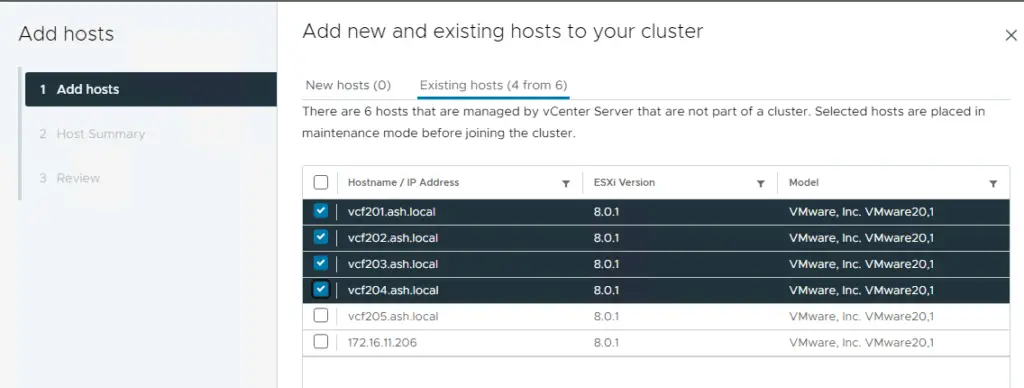
5. Select all four hosts for VSAN cluster.
6. Once the wizard is completed, you can see the cluster summary as shown. Select the Finish button to add hosts to the cluster.
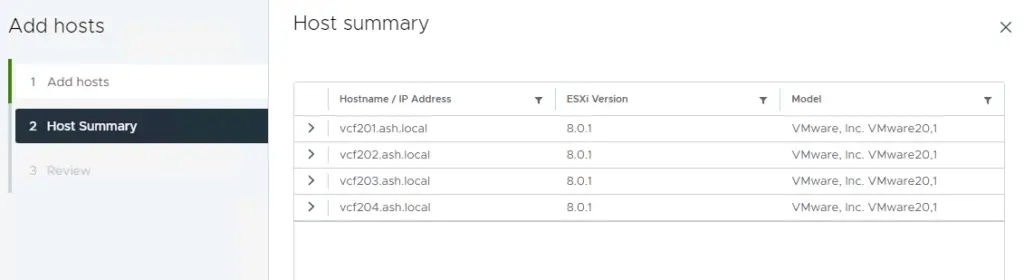
7. We can now see all our hosts added to the cluster
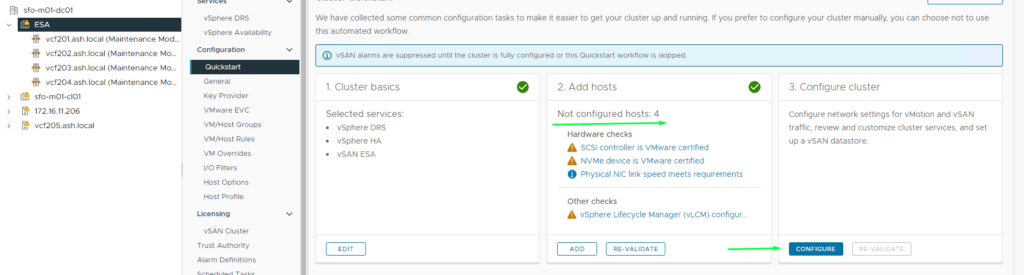
8. Click on the Configure tab to add the hosts to vSAN services. In the next screen, we will be presented with a window to create a distributed switch but we will be using our distributed switch.
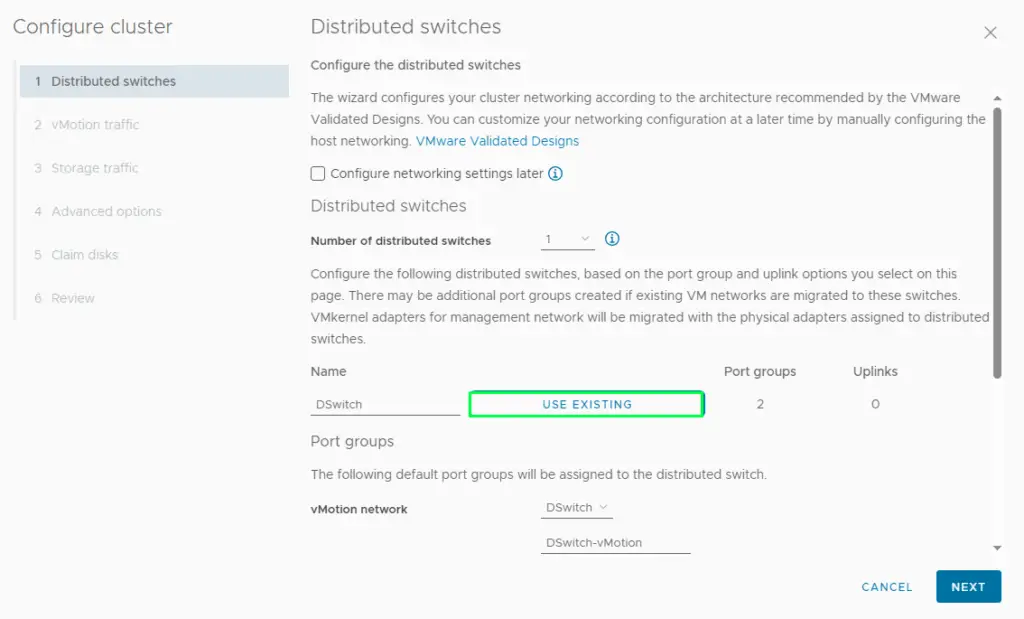
9. Click on the existing distributed switch
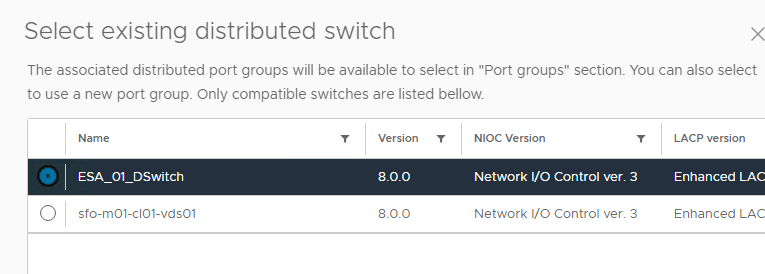
10. Click on the existing distributed switch, choose the vSAN and vMotion port groups we created earlier and select both the uplinks on our host.
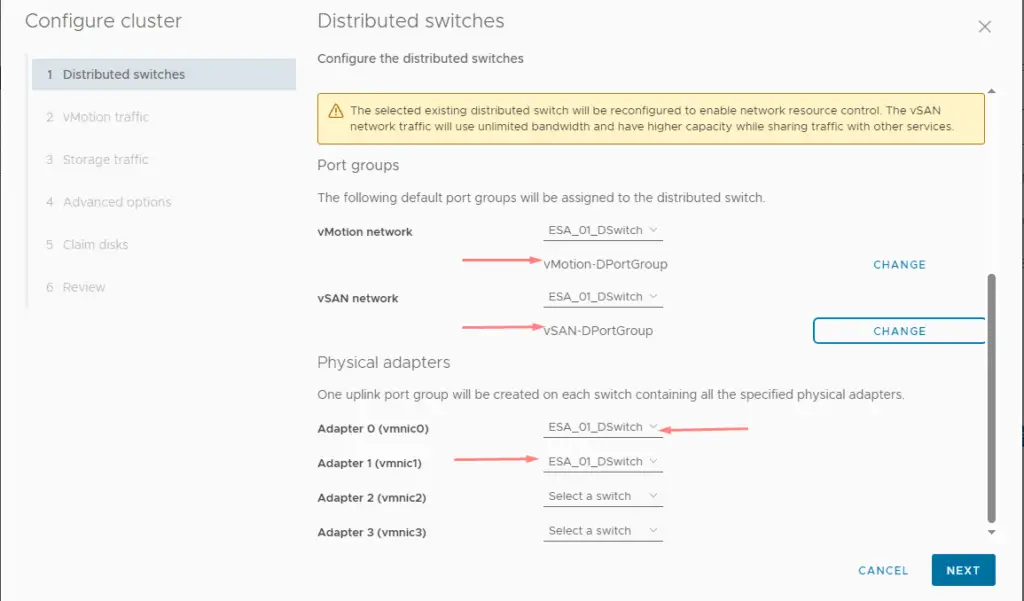
11. For vSAN to work, we need a dedicated vmkernel adapter to enable vMotion services. Add the IP address for our vMotion network

12. For vSAN to work, we need a dedicated vmkernel adapter to enable vSAN services. Add the IP address for our vSAN network
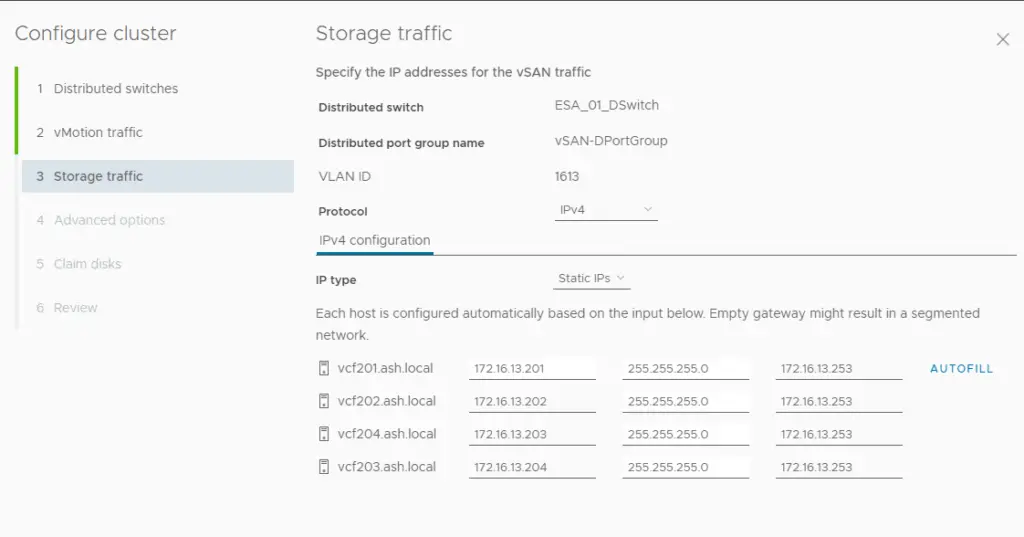
13. For vSAN to work, we need a dedicated vmkernel adapter to enable vSAN services. Add the IP address for our vMotion network
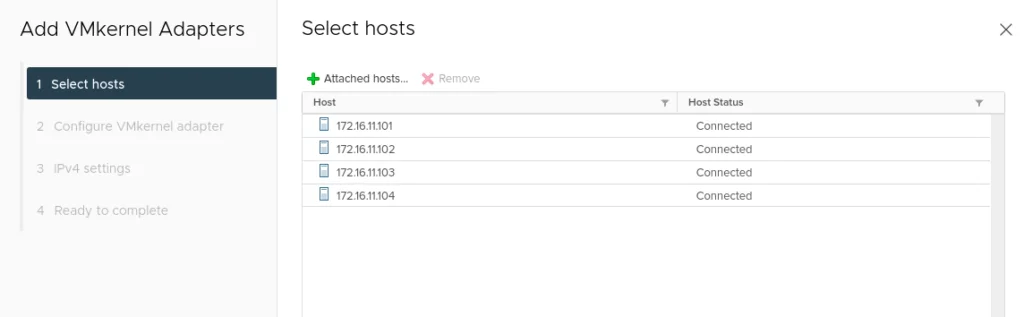
14. In the next screen, we have an option of enabling the following services on the vSAN datastore
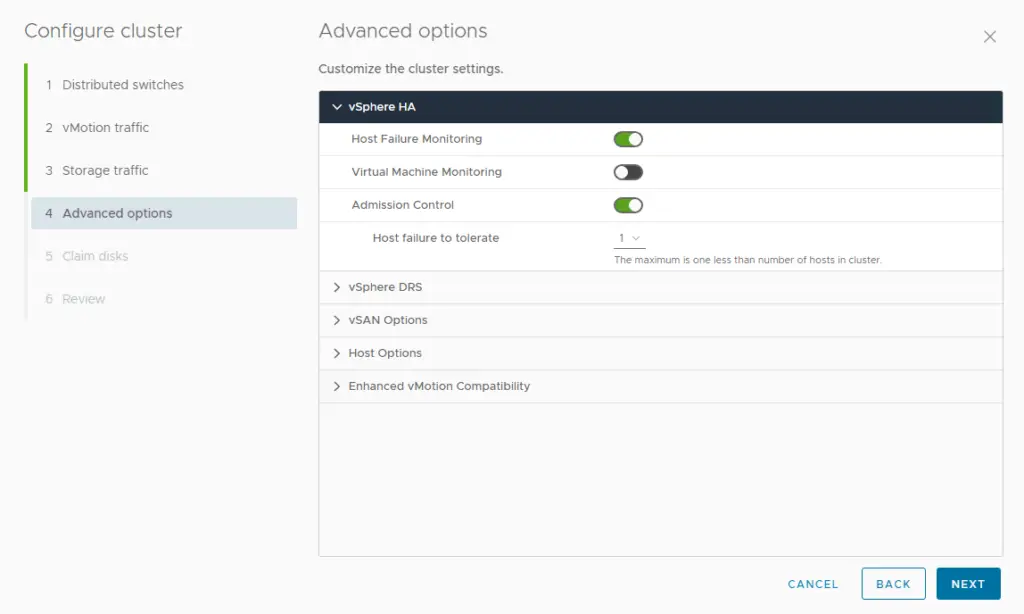
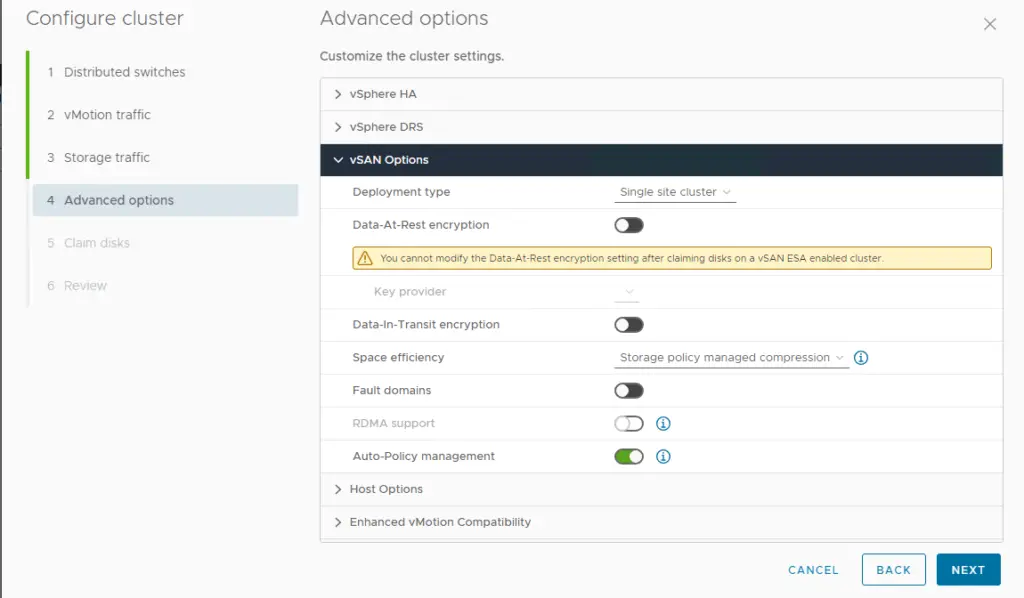
15. Choose the vSAN configuration as Single site cluster
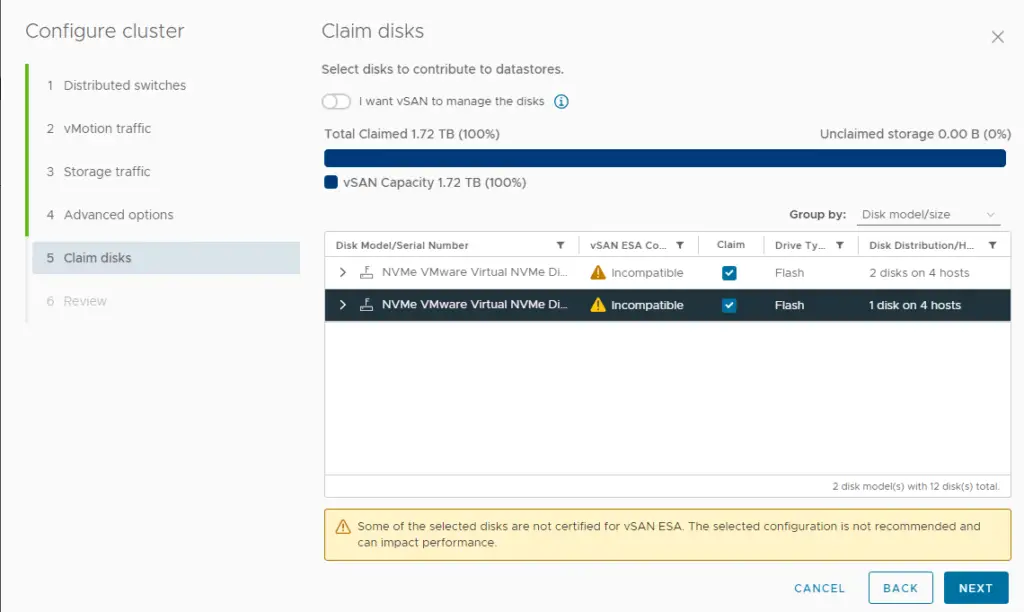
16. Choose to claim disks that will contribute to the vSAN datastore and then click next.
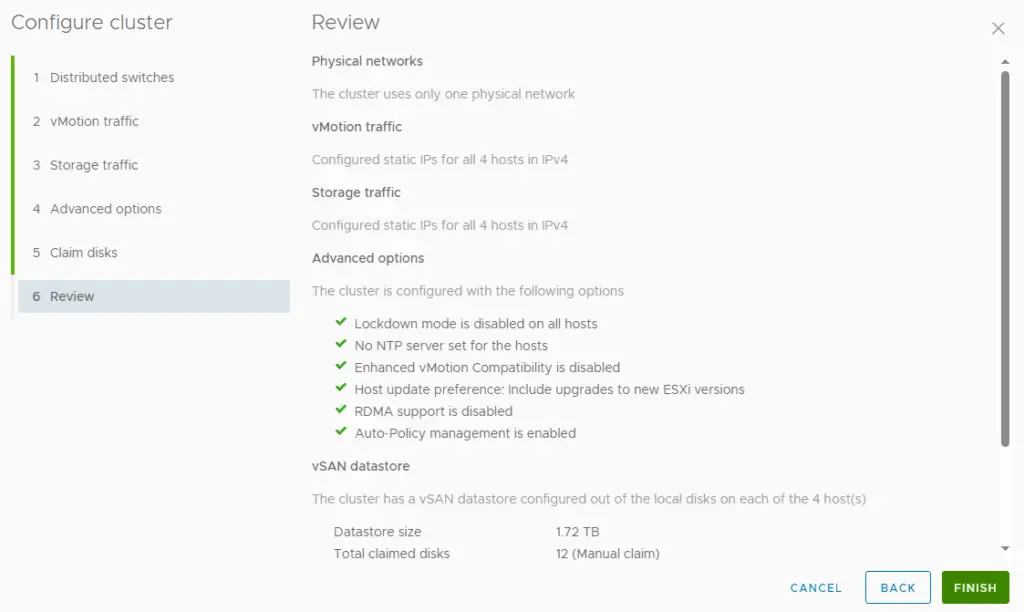
17. Review the vSAN cluster settings and then click finish.
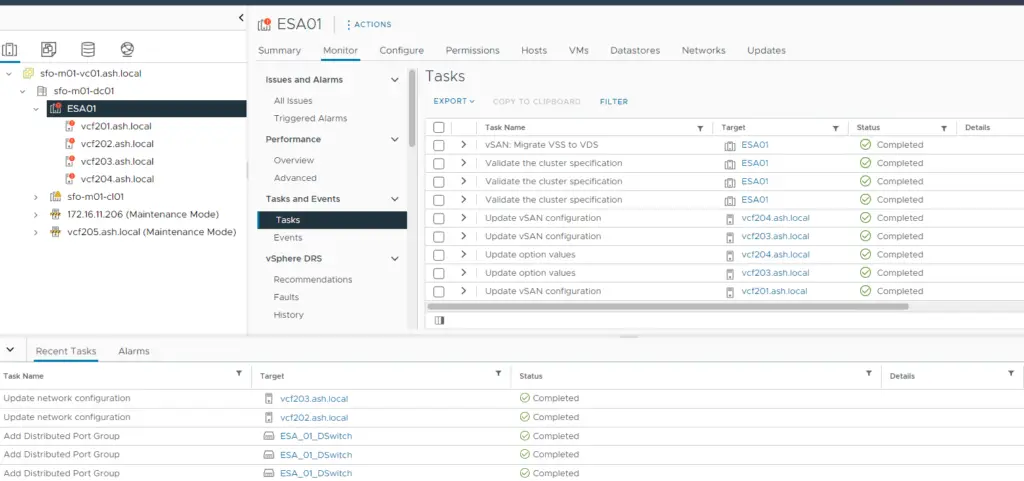
18. vSAN cluster creation tasks can be viewed under the events section
19. Once the vSAN Cluster creation is done, we can see on our host’s side that two disks on the host are participating in the vSAN datastore
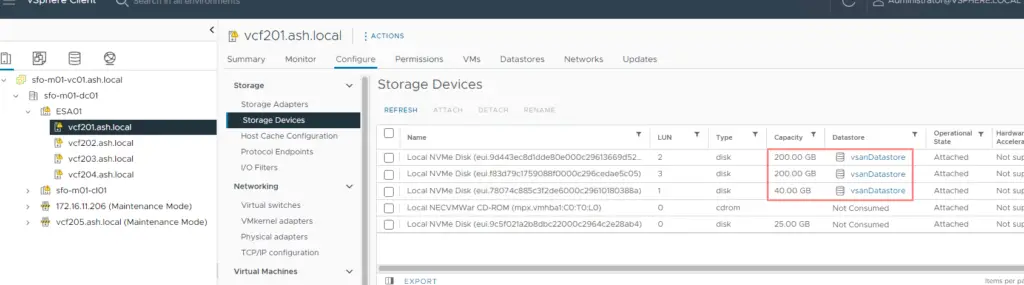
20. vSAN Status can be monitored via the Monitor tab which shows the Capacity used and the Capacity reserved for vSAN Metadata

We have successfully configured the VSAN ESA cluster.

