While DFW exists and enforces rules at the vNIC level of every VM saying “Who can talk to whom” inside the datacenter and its perfect for east‑west traffic enabling micro‑segmentation the Gateway Firewall exists to see “What comes in/out” of the datacenter or tenant.
So the Gateway Firewall extends NSX’s distributed firewalling capabilities to the Tier‑0 (T0) and Tier‑1 (T1) gateways, enabling granular control over north‑south traffic flows. This layered approach ensures that workloads are protected at the edge, within tenant boundaries, and across application tiers.
Gateway Firewall ensures north‑south enforcement before traffic even reaches workloads.
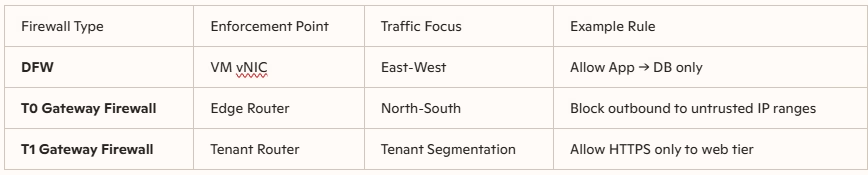
Lets take an example here, to configure a GW Firewall policy both at the TO and T1 GW.
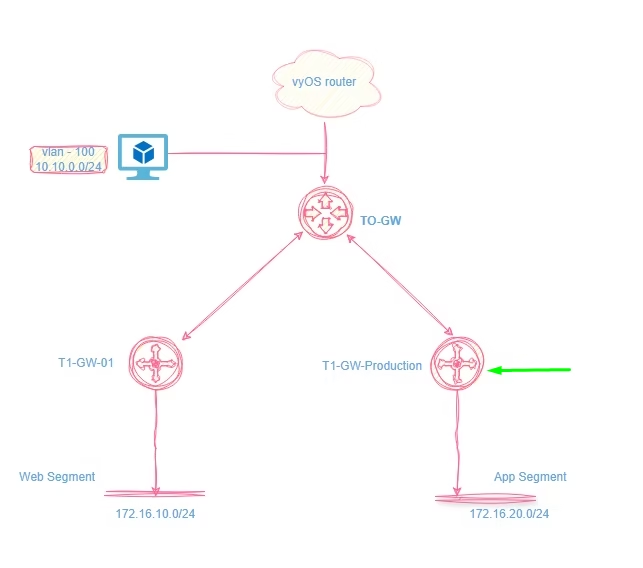
NSX Routing Architecture Recap
- Tier‑0 (T0) Gateway
- Connects the NSX environment to the physical network.
- Handles north‑south traffic (inbound/outbound to external networks).
- Provides high availability and scalability for data center edge connectivity.
- Tier‑1 (T1) Gateway
- Connects logical segments (VM networks) to the T0 gateway.
- Handles east‑west traffic between workloads and north‑south traffic within tenant/application boundaries.
- Supports services like NAT, DHCP, and load balancing.
Gateway Firewall can be implemented in two areas
- Tier‑0 Firewall
- Enforce data center edge security so its for controlling traffic between NSX and external networks.
- Best placed for global rules (e.g., block all outbound to untrusted IP ranges).
- Tier‑1 Firewall
- Enforce tenant‑level segmentation.
- Best placed for global rules (e.g., block all outbound to untrusted IP ranges).
Enforce datacenter edge security at the TO-GW
Our environment consists of a classic three‑tier application: client → web → app → DB.
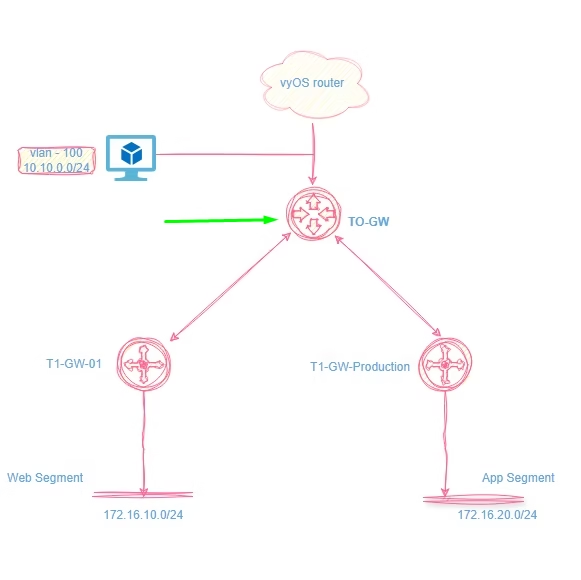
Navigate to Inventory > Groups > New Group > Name the group 3-tier-app-servers.
Click on Compute Members
Under Membership Criteria: Criterion 1: Virtual Machine Tag =3 tier
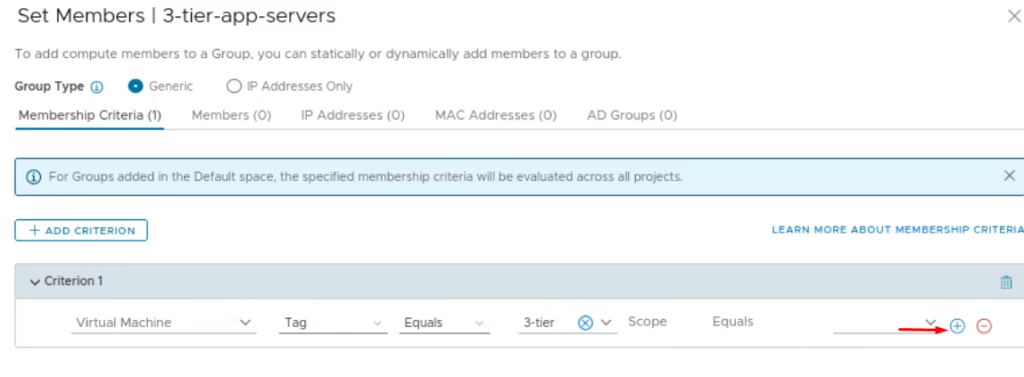
Set the AND criterion as Tag Equals app
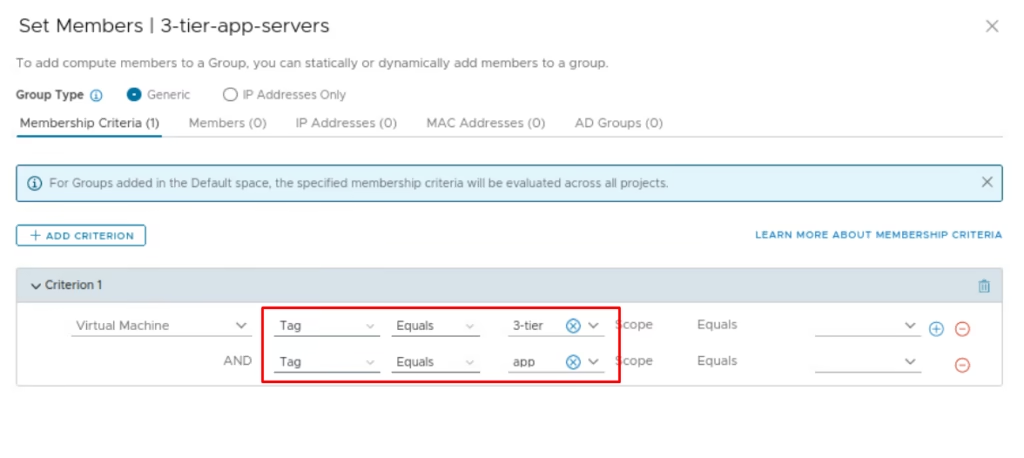
Click Save and Repeat for web and DB servers with appropriate tags.
Go to Gateway Firewall → Select the Gateway as TO-GW .
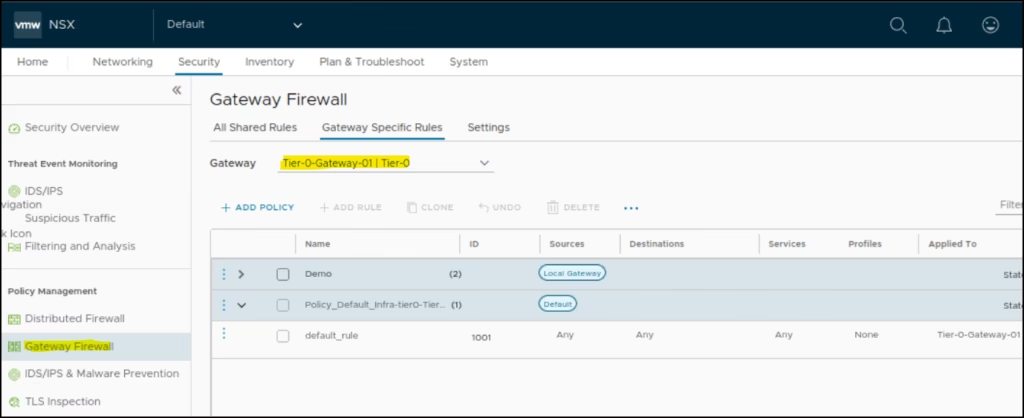
For our TO-GW-access rule only to allow all HTTP traffic sourced from anywhere and going to our 3 tier web server, we create a simple rule as “The T0 GW Http policy”
Rule1 settings:
- Name: Allow http to prod web segment
- Sources: Any
- Destinations: 3-tier-web-servers
- Services: HTTPS/HTTP
- Applied to TO-GW
- Action: Allow
Rule2 settings: This is done to allow all traffic other than http to pass through
- Name: Deny other traffic to prod web segment
- Sources: Any
- Destinations: 3-tier-web-servers
- Services: Any
- Applied to TO-GW
- Action: Allow
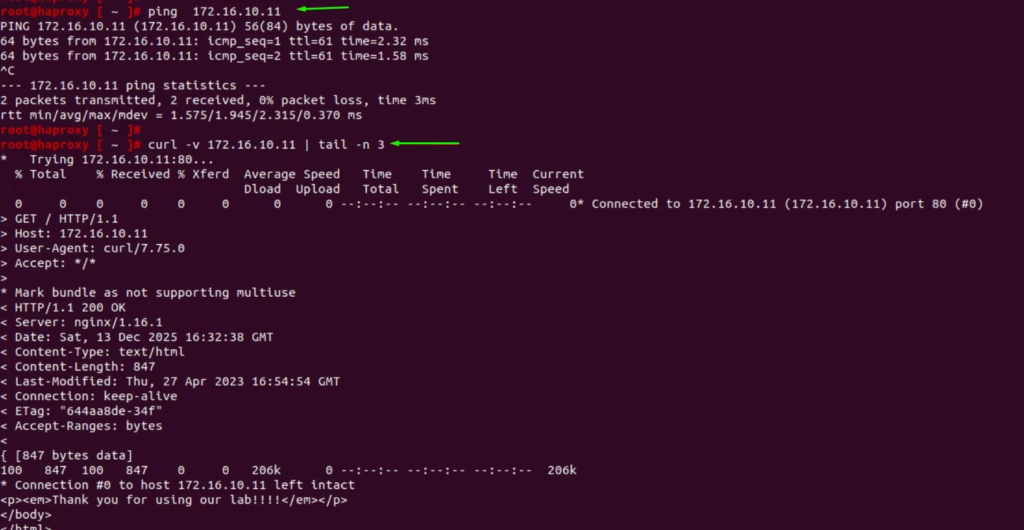
Run a ping and curl test and it now passes through
Under Rule2 settings: Block all other traffic other than 80 and 443
- Name: Deny other traffic to prod web segment
- Sources: Any
- Destinations: 3-tier-web-servers
- Services: Any
- Applied to TO-GW
- Action: Block
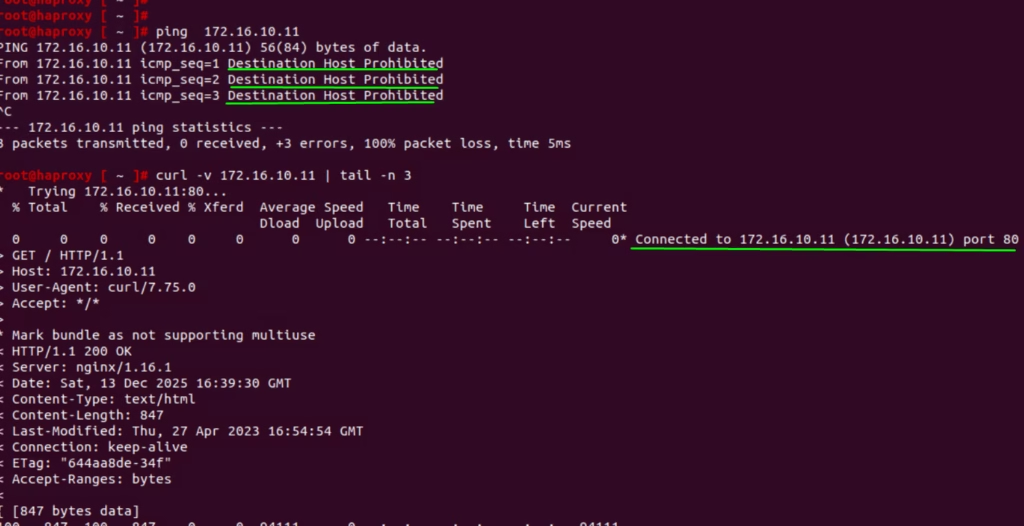
The ping test fails so this validates our rules are working at the gateway level.
The logs shows the traffic on it
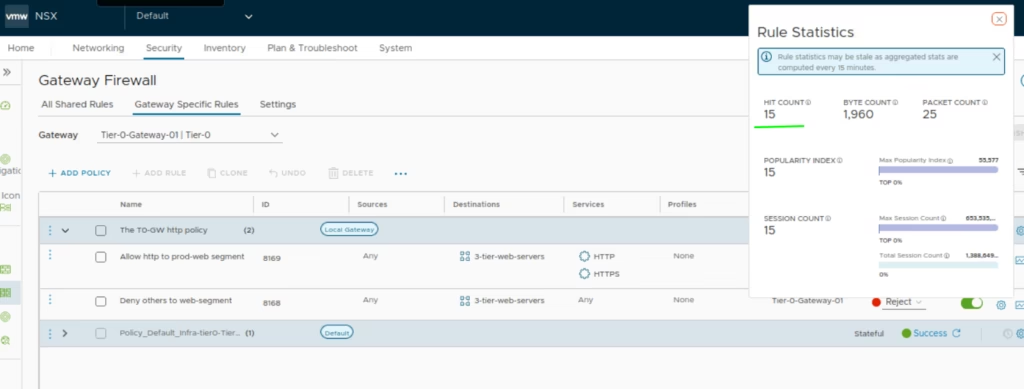
Enforce datacenter edge security at the T1-GW
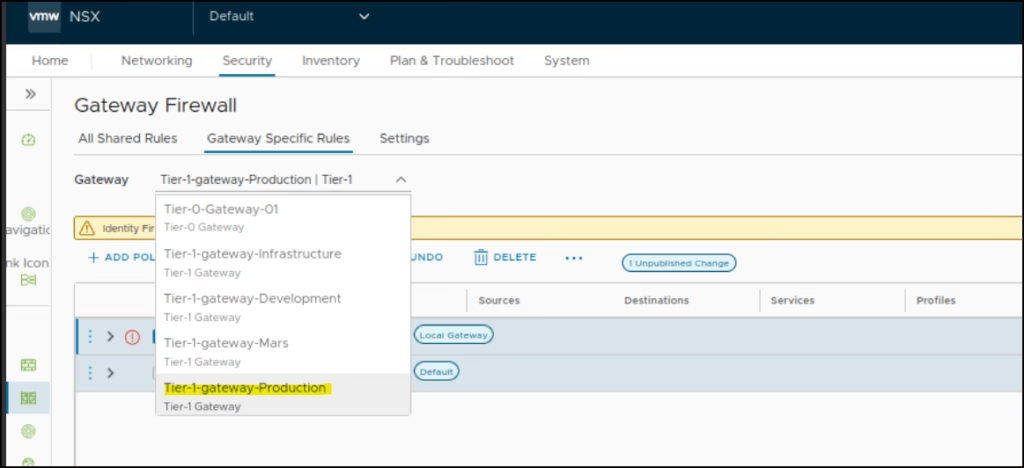
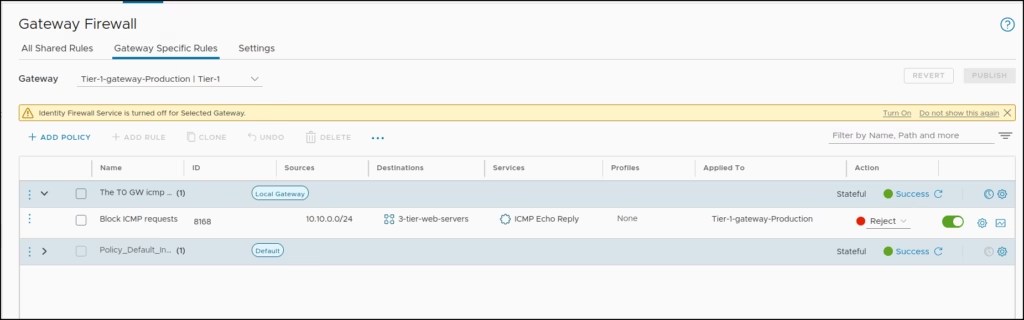
Go to Gateway Firewall → Select the Gateway as T1-GW-Production
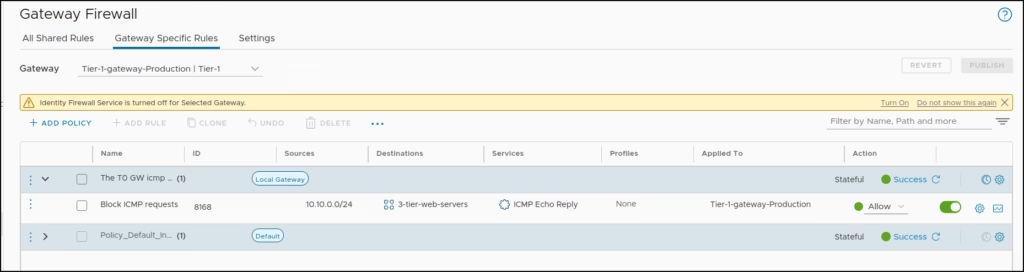
For our T1-GW Production – access rule only to block ICMP traffic sourced from anywhere and going to our 3 tier web server, we create a simple rule as “The T0 GW icmp policy”
Rule1 settings:
- Name: Block ICMP requests
- Sources: Any
- Destinations: 3-tier-web-servers
- Services: ICMP Echo Reply
- Applied to Tier1-Gateway-Production
- Action: Allow
Run a ping and it now passes through
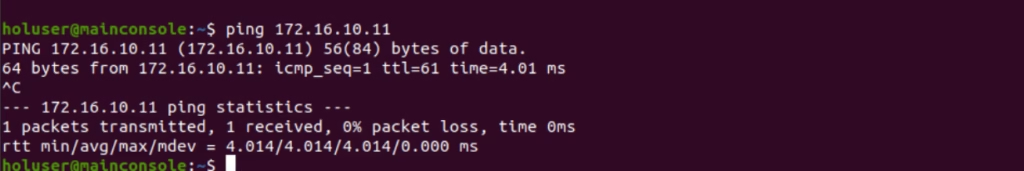
Click Save and Publish the rules
The ping test fails so this validates our rules are working at the gateway level.
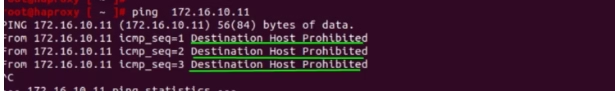
An important point to note is that rules applied to a Tier-1 (T1) Gateway are specific to that gateway. If a ping still works from a segment that shouldn’t be able to ping, check the edge gateway’s status to see if it is set to Active/Standby. Sometimes, the edge on another T1 Gateway may be pointing to a different edge node (e.g., Edge 2), which can affect rule enforcement.

