If there is no adjacent Unallocated space on the right side, when you right-click C drive, you’ll find that the Extend Volume is greyed out. In our scenario, the recovery partition is preventing us from extending the drive and it can also be due to one of the following reasons:
- The complete partition needs to be reformatted in NTFS because the existing FAT/FAT32 format cannot be extended.
- No other dynamic disk has any unallocated space on it.
- On the same basic drive, there isn’t any continuous unallocated space to the right of the partition.
What is Recovery Partition?
A recovery partition is a feature of the Windows operating system that is utilized for system recovery. If OEM recovery partitions are measured in gigabytes, but Windows recovery partitions are typically measured in megabytes(500MB).
Windows operating system has four different types of partitions by default when its built.
- Recovery
- System
- Reserved
- Primary
Recovery Partition
The recovery partition in Windows Server 2019 has a size of 499 MB. This partition on the system hard drive—is utilized to return the system to its original configuration.
System Partition (Hardware Config)
The system partition in Windows Server 2019 has a size of 100 MB. System partitions are required by Windows to load the operating system’s hardware-specific files. Another name for it is the system partition known as EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface). The file saved on Extensible Firmware Interface is loaded by the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface firmware as soon as your machine turns on, setting up your operating system and other system functions.
Reserved Partition (Boot Info)
The system partition size in Windows Server 2019 is 16 MB and they are used to hold Windows boot configuration data.
Primary Partition (C:)
The operating system files that are loaded into a computer upon startup are located in a primary partition.
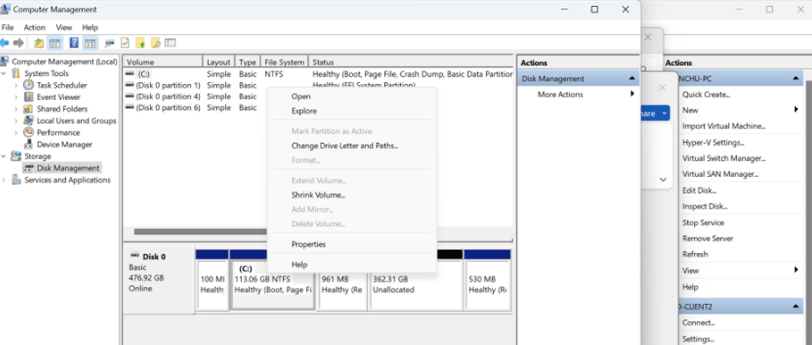
As per output, the Recovery Partition is located in HDD0 with partition 4.
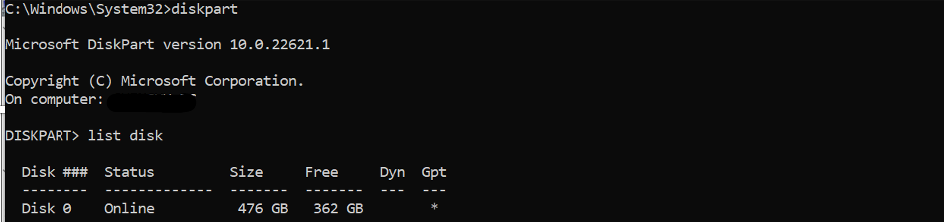
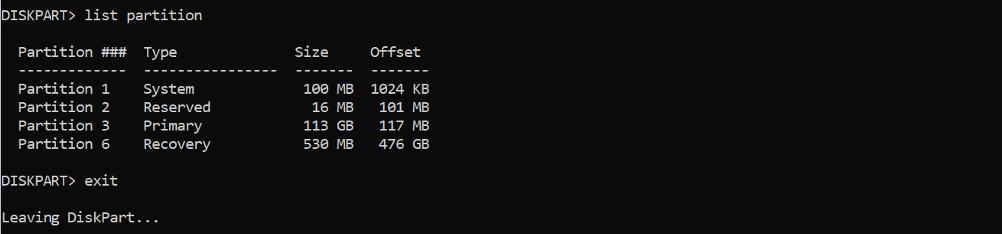
Use DiskPart command to see the disk layout
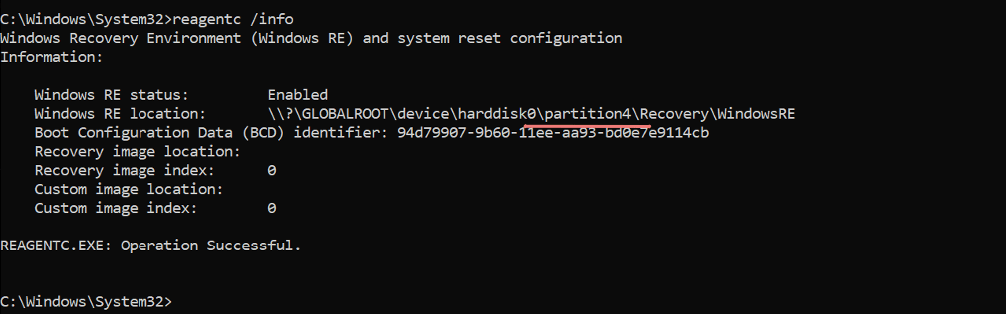
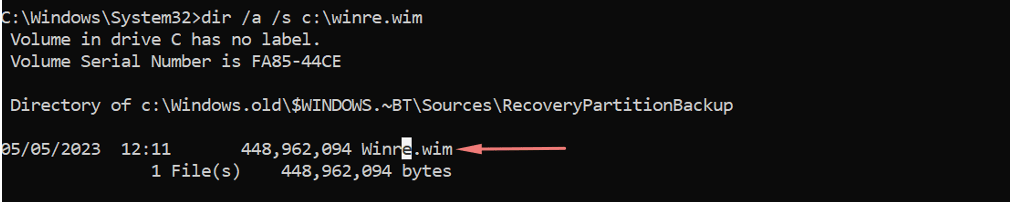
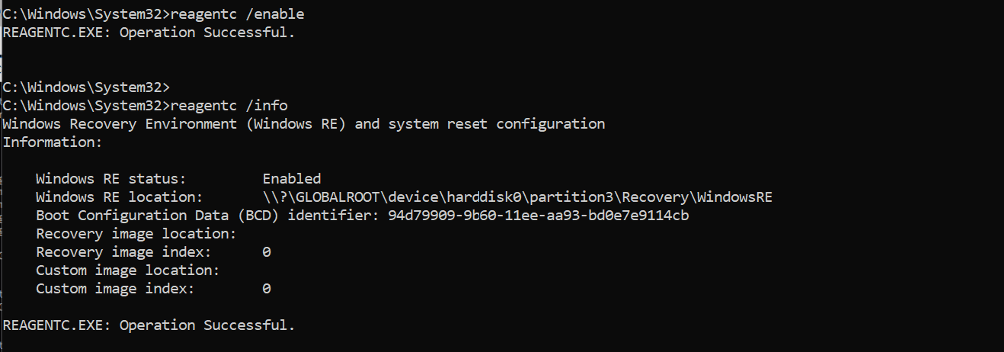
Run reagentc /info command to check the status of Windows Recovery Environment. If this output shows it’s enabled, just run the command reagentc /disable. “Windows Recovery Environment” (WinRE) is an experience that offers features like automatic repair, factory reset, system image recovery, and other troubleshooting tools to resolve issues when your computer doesn’t start correctly. This file is usually available under the hidden folder C:\Recovery so ensure you copy and save this file.

Select the Disk that has the OS on it.
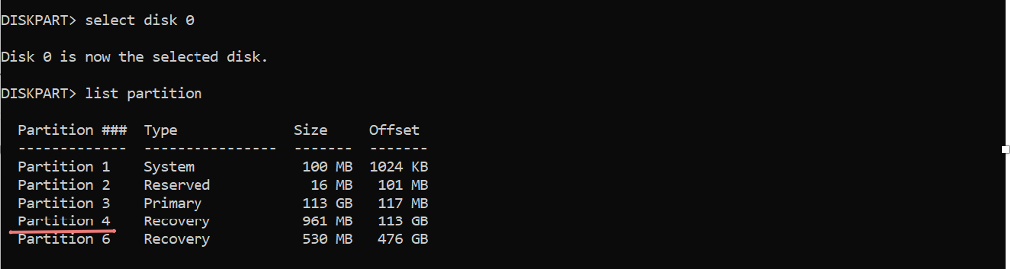
Select the partition

Delete the recovery partition

List the available partition
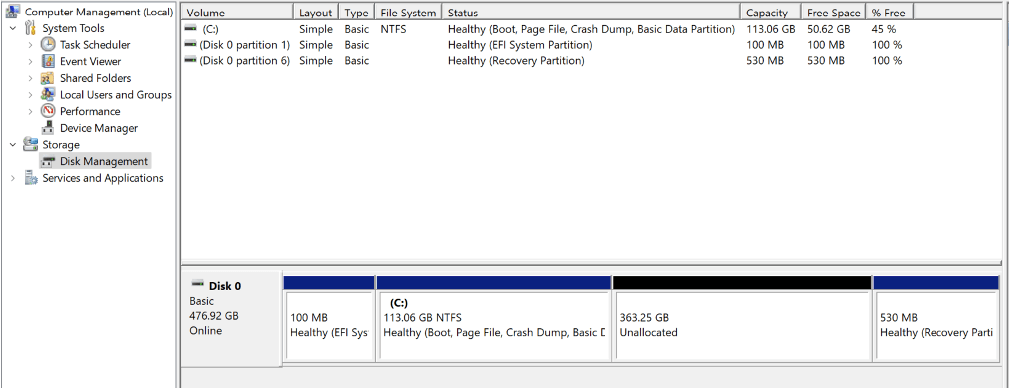
We should now be able to extend our drive as usual.
Enable Windows Recovery Environment
Run reagentc /info and hit the Enter key to execute it.

Copy the file from this location and put it back in the hidden folder C:\Recovery. You can also get this from the ISO image.
Run reagentc /enable and hit the Enter key to enable the Windows Recovery Environment
Diskpart Delete Partition Override Virtual Disk Error
You might hit this error on Hyper-V-based VMs as you try to delete the partition.
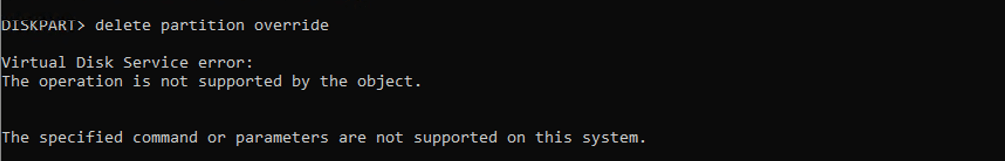
Run the command reagentc /disable. “Windows Recovery Environment” (WinRE) is an experience
Download the latest distribution of Zorin/Ubuntu Desktop ISO and boot the VM with the ISO file . Once the VM boots up, click “Try or Install Ubuntu/Zorin“.
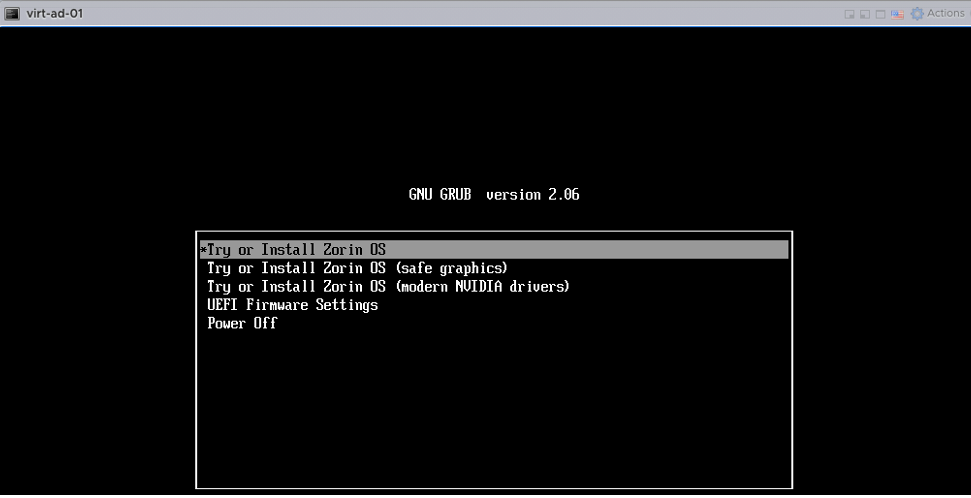
Click “Try or Install Ubuntu/Zorin“.

Launch the Disks app from the settings menu and highlight the extra 550 MB partition next to the free space.
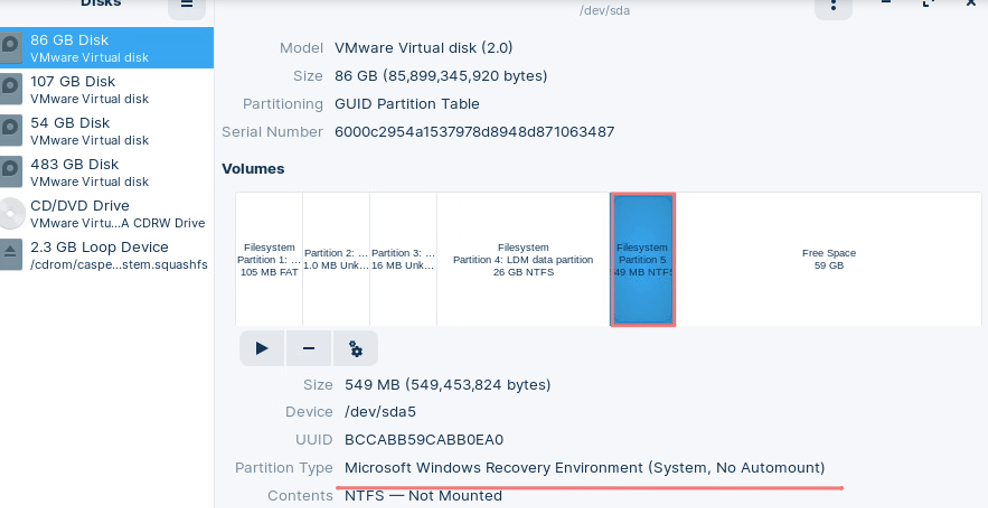
Click Delete to confirm you wish to delete the extra recovery partition.
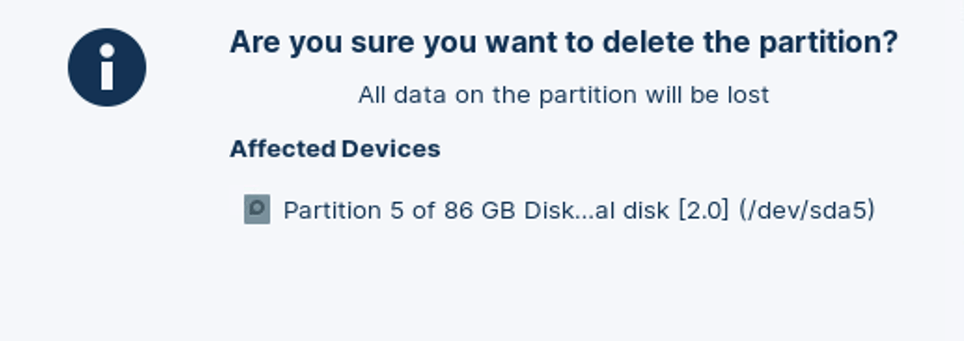
The recovery partition is now deleted as shown.

Umount the ISO and Reboot to the Windows Server OS and you should be able to extend the disk as usual.

