Edge nodes are an On/Off ramp for Overlay Networks. It’s a bridge between the outside and the NSX-T internal world. Edge is responsible for communicating with the top of rack switches.
An edge is an appliance that can run multiple virtual routers.
Provide routing services:
- East‑West routing (within NSX).
- North‑South routing (to/from external networks).
- Work with Tier‑0 and Tier‑1 routers to deliver full routing functionality.
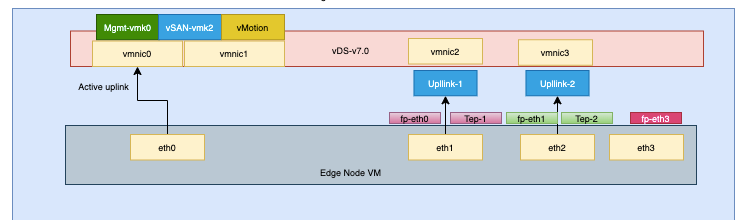
Edge VM Architecture
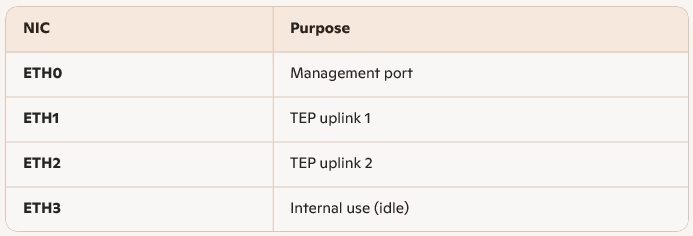
An edge VM will have 4 NICs once deployed, these are also called fast path adapters.
Checklist before deploying Edge
- Max of 10 edge nodes are supported in a cluster.
- Jumbo MTU enabled on vDS of host
- Configure uplink profile for edge nodes
- IP Pool for Edge TEPs (can share with host TEPs in NSX‑T 3.1+).
- VLAN IDs defined for upstream router connectivity (configured both on physical network and vSphere port groups).
- Management VLAN /IP for Edge
- TEP VLAN defined (can be same as host TEP VLAN in lab, but separate in production).
- L3 reachability between host TEPs and edge TEPs.
Let’s check the NSX egde VM form factor and its compute requirements.
| Appliance Size | Memory | vCPU | Disk Space |
| Small | 4 | 2 | 200GB |
| Medium | 8 | 4 | 200GB |
| Large | 32 | 8 | 200GB |
| Extra Large | 64 | 16 | 200GB |
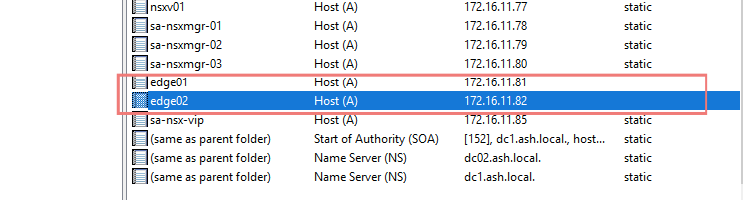
Create a DNS record for the new EDGE VM.
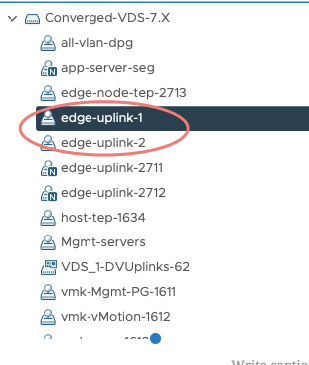
Define distributed port groups for our edge uplinks
These are defined in the distributed port groups.
Create two port groups to connect the fast path interfaces to the physical switches in trunk mode, this can also be done on top of the vDS but here this is done at the portgroup level.
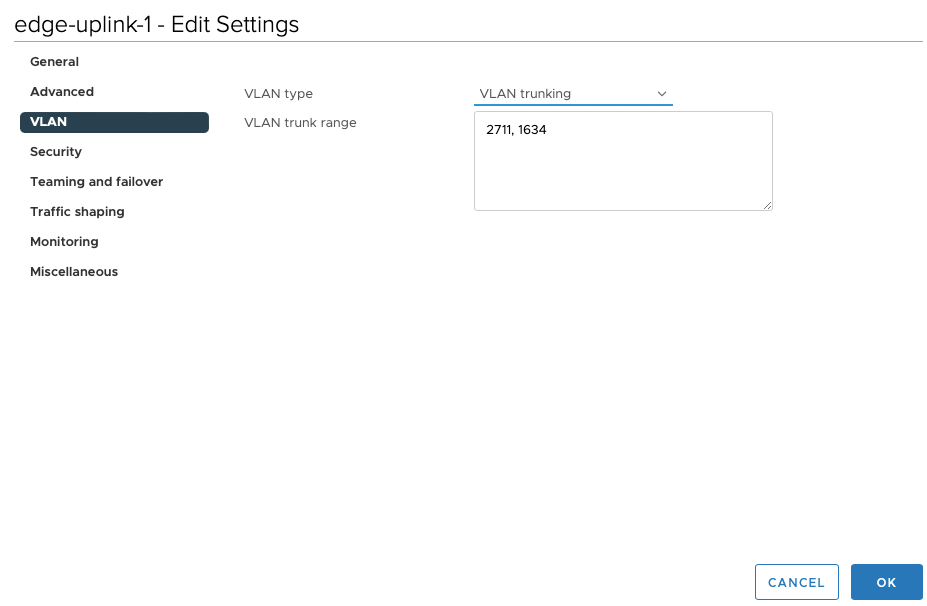
Under edge-uplink1 i’ve the below config to show uplink 3 is my active interface
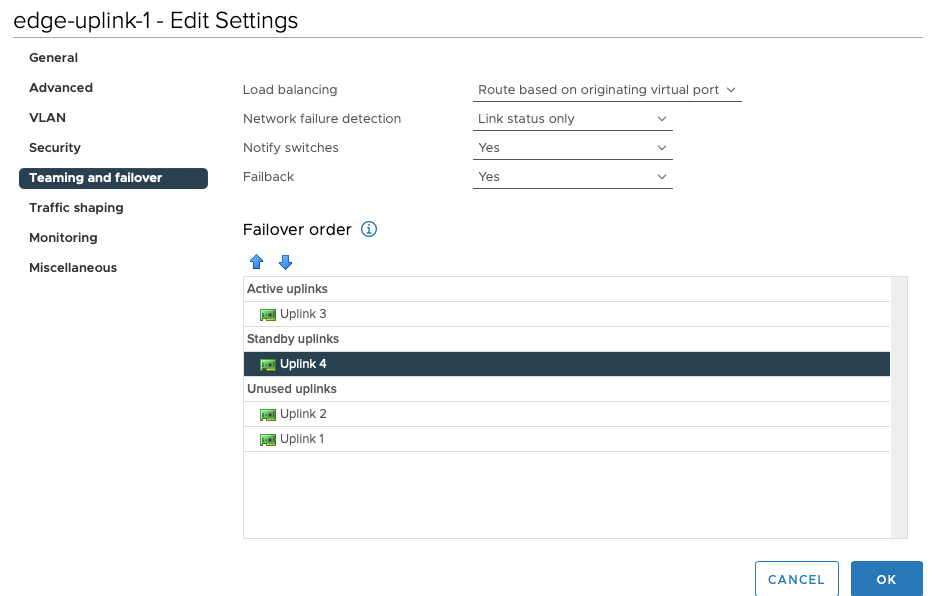
Under edge-uplink2 i’ve the below config to show uplink 4 is my active interface and uplink 3 as standby
Creating Edge Cluster
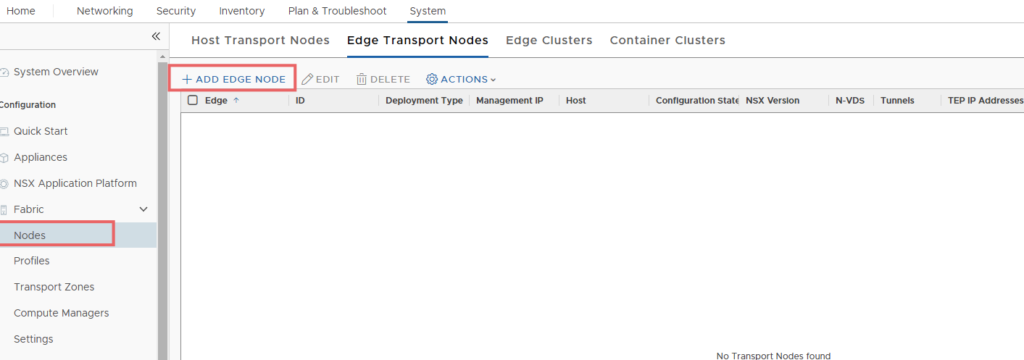
On the NSX UI Home page, navigate to System > Configuration > Fabric > Nodes > Edge Transport Nodes
Provide Name, FQDN & Select Form Factor as ‘Medium’
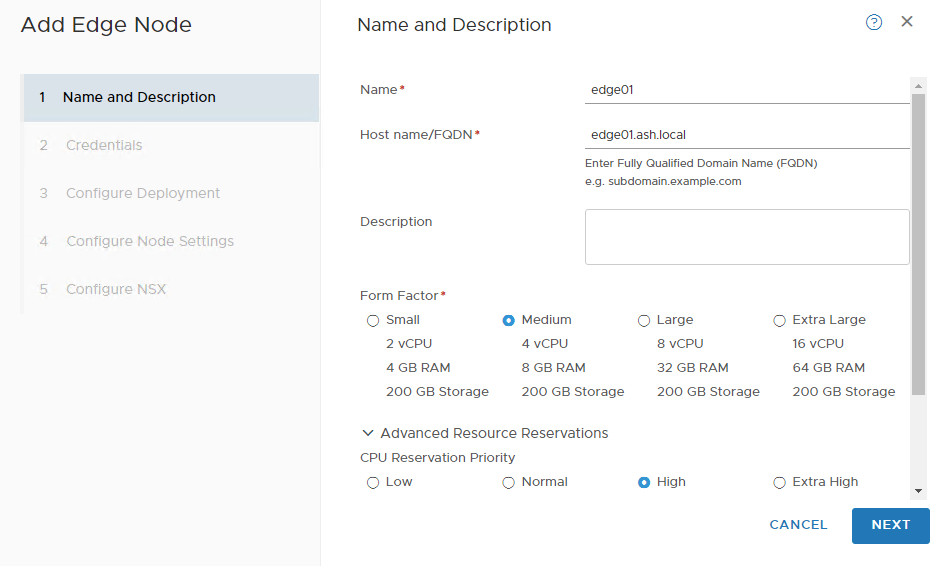
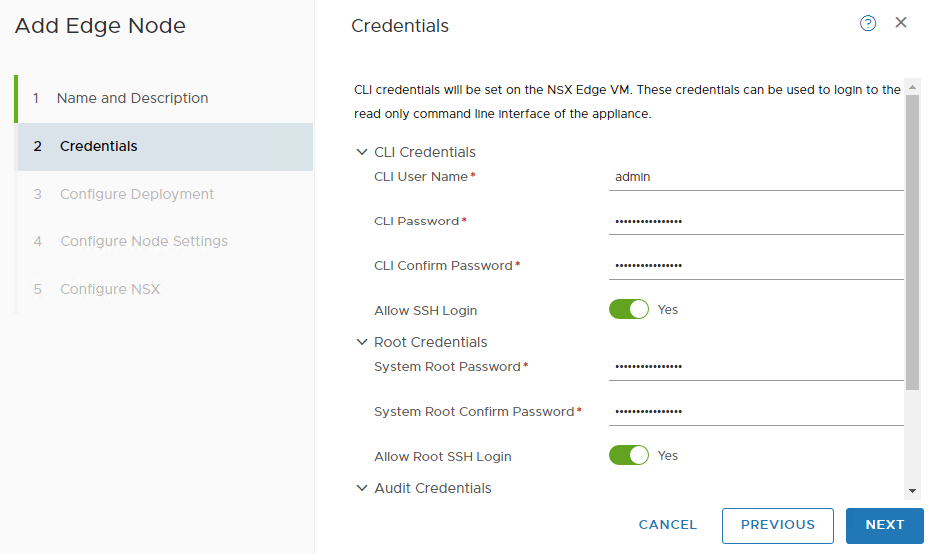
Set the password for CLI and Root User. Make sure to set the password according to password policy.
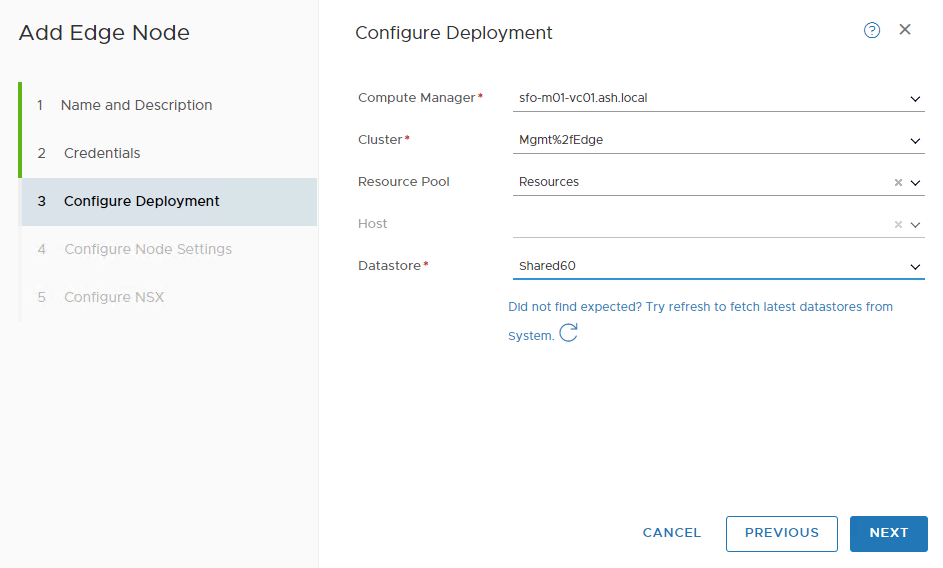
Select Compute Manager, Cluster & Datastore.
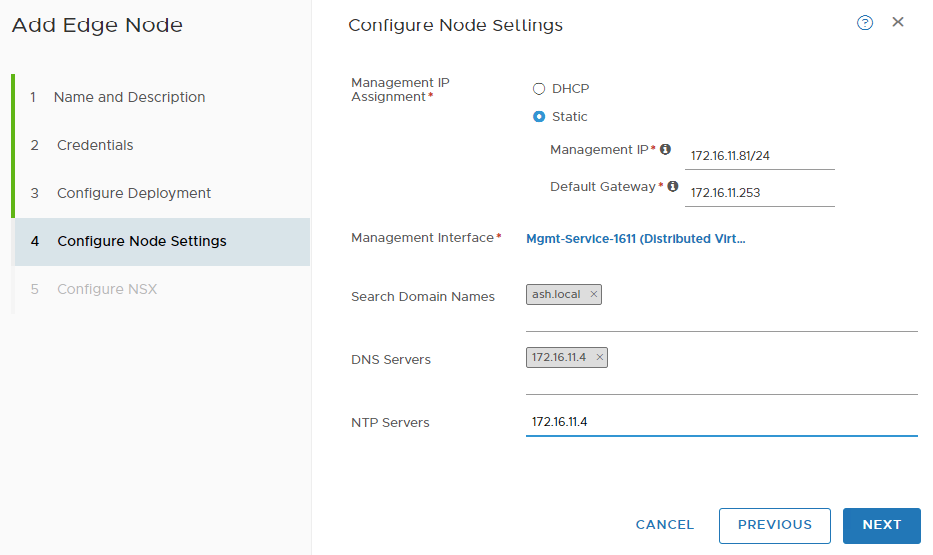
Select Static and enter Management IP & Gateway. Click on ‘Select Interface’ and Select your management network.
Enter the remaining information and click Next.
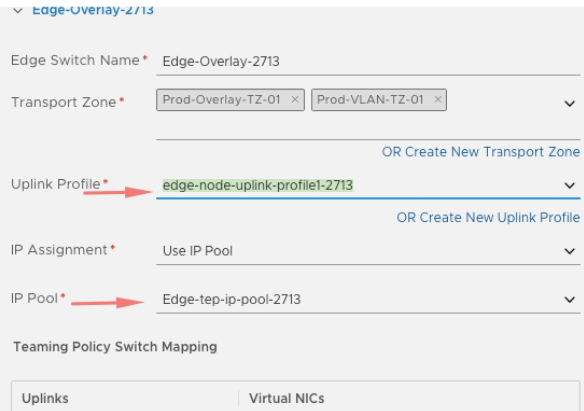
- Name:
Prod-Edge-Switch. - Transport Zones: select both Overlay & VLAN TZs.
- Uplink Profile:
edge-node-uplink-profile-2713. - IP Assignment:
edge-tep-ip-pool-2713.
Fill out gateway and subnet mask and move to next section.
Map your Edge uplinks with the Uplink port groups that you have created in your vCenter.
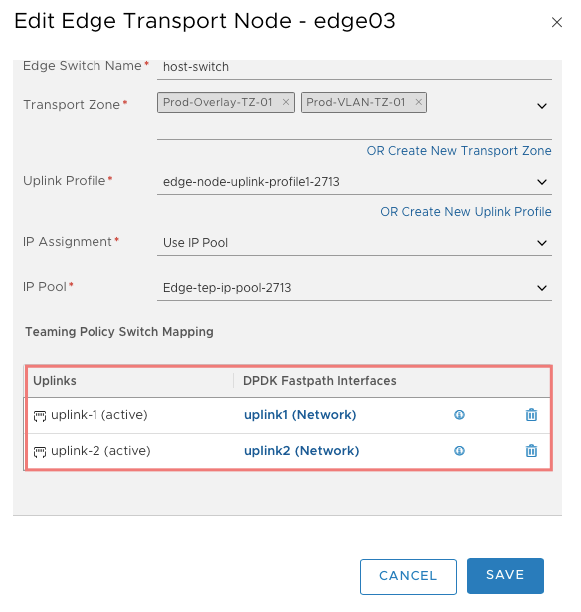
We will use an IP address from these uplink port groups to form BGP neighborship with TOR when we create Tier-0 router.
Click Finish and check if you see a VM getting deployed in vCenter.
The physical interfaces are shown

Edge VM will appear under ‘Edge Transport Node’
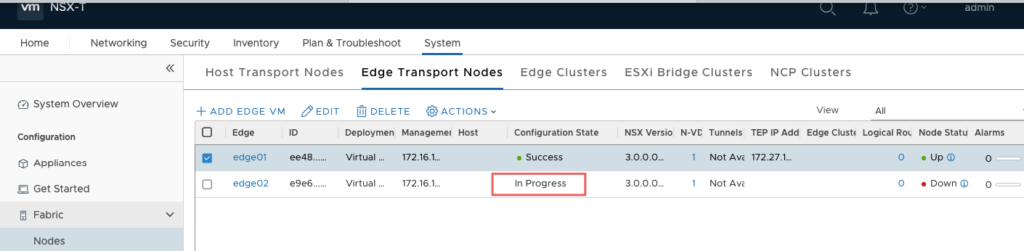
Monitor the status.
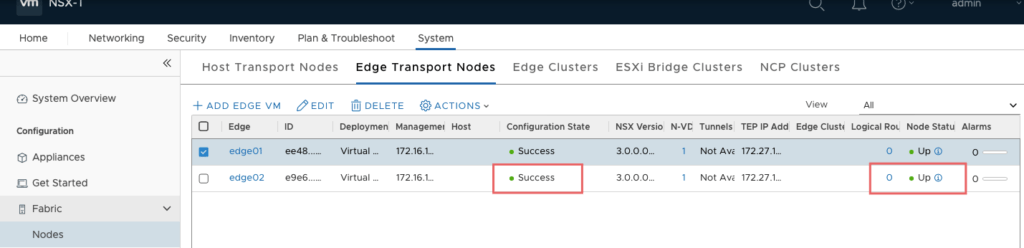
Creating Edge Cluster
Edge VM has been installed and configured successfully. We now move to Edge Cluster.
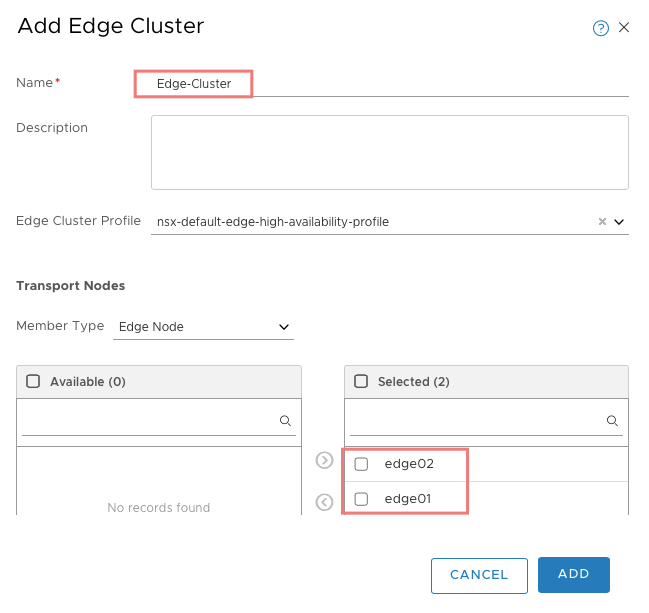
Navigate: System → Nodes → Edge Cluster → +ADD.
- Name:
Edge-Cluster. - Edge Cluster Profile: Default HA profile.
- Transport Nodes: move
edge01&edge02from Available → Selected.

Name: Edge-Cluster
Edge Cluster Profile: Default profile is selected automatically.
Transport Node: Move edge01 & edge02 from Available to Selected.
Click Save.
We are done with creating Edge Cluster. This cluster will be used when we create Tier-0 Router.
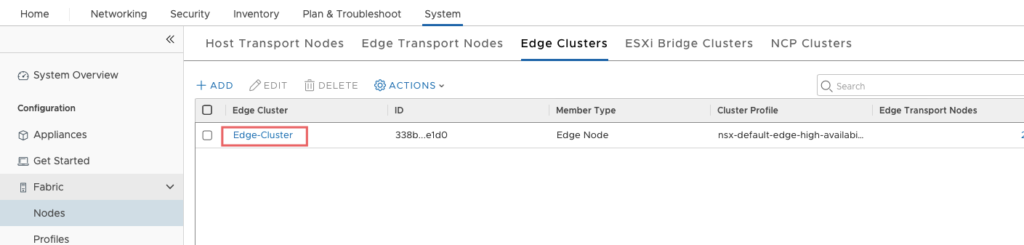
Next step: Tier‑0 Router creation, leveraging the Edge Cluster for BGP peering with TOR switches.

