In this series, we are going to enable VXLAN port and prepare our hosts for receiving VXLAN traffic.
Blog Series
- Installing NSX-V 6.4
- Configure Controller Nodes and enable CDO mode in NSX-V 6.4
- One Page View of all NSX-V commands
- Configure VXLAN and Prepare ESX hosts for VXLAN traffic
- Configure the Transport Zone and Logical Switches
- Configure Distributed Logical Router
- Configure Edge Services Router (ESG)
- Verifying VXLAN Connectivity
- Regenerate Self-signed Certificate on NSX-V
- DLR VM SSH Access
- Backup NSX-V Manager
- Dynamic routing with OSPF in DLR
- Dynamic routing with OSPF in ESG
- VMware NSX Edge Load Balancer
- VMware NSX Edge Load Balancer SSL Offloading
- NSX-V Firewall & Microsegmentation
In the Installation and Upgrade > Logical Networking Settings – Configure the VXLAN Port by click Edit and configure the VXLAN port (4789) which is the default.
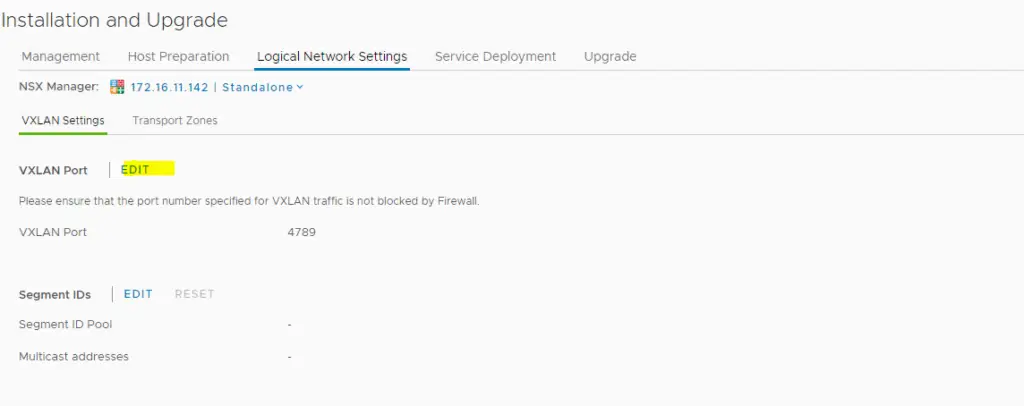
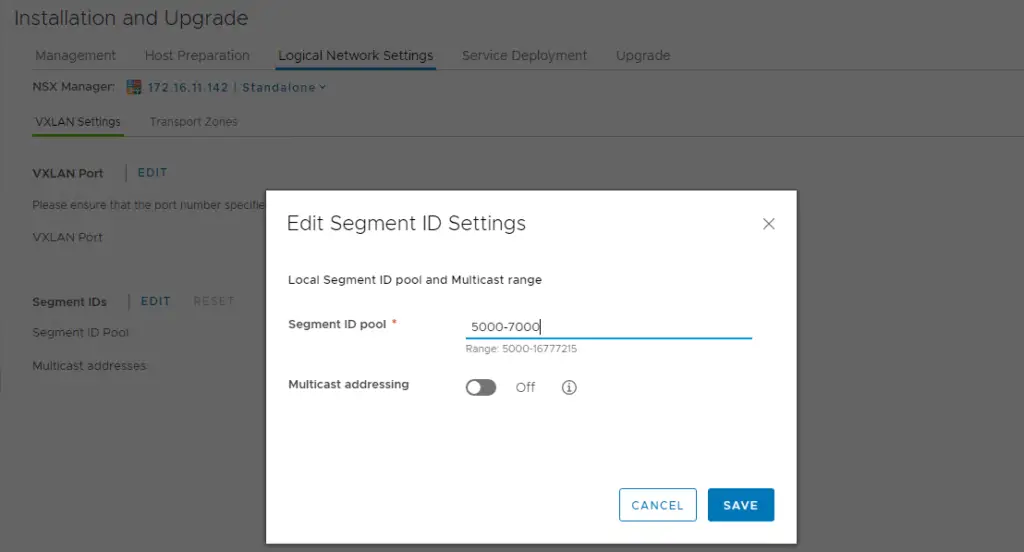
Choose the segment ID pool which is actually a range of permissible VLAN range for corelating it.
We provide our logical switches in NSX this segment ID to seperate traffic.
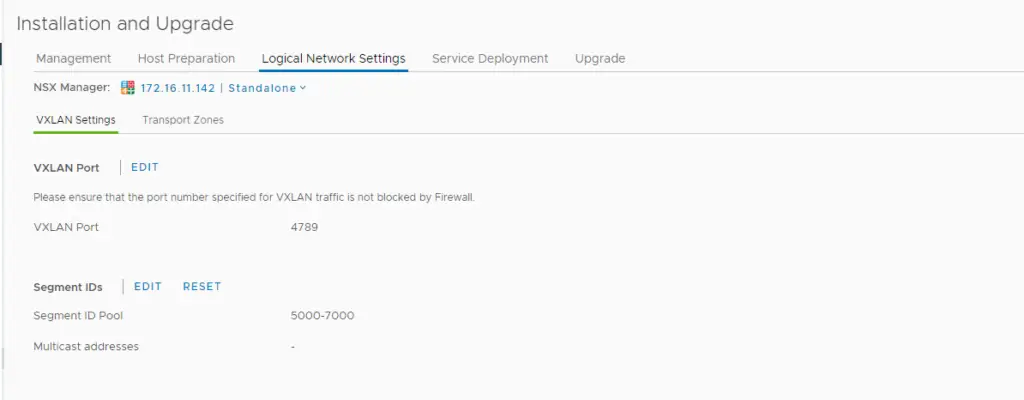
Save the config and we will be presented with this screen
Prepare the ESXI Hosts for the NSX
Host preparation means installing NSX packages also known as vibs to each of the esx hosts within the cluster to enable the functionality of all NSX features on esx hosts such as VXLAN, distributed firewall, distributed routing etc.
Select Host Preparation and pick the cluster that includes the hosts that need to be prepared for the NSX workloads.
When we click Install NSX, this will push install the NSX vib’s to our esx hosts.
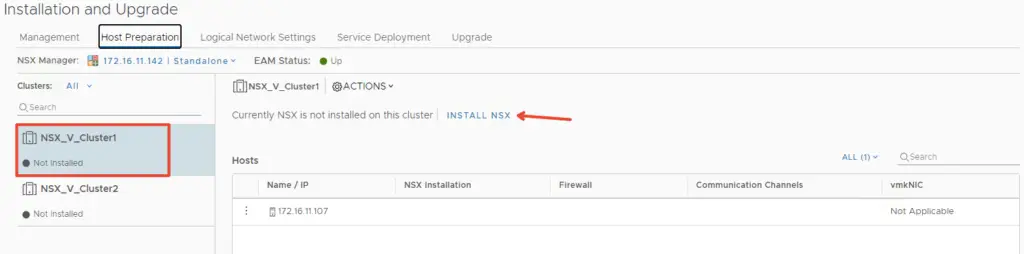
Click yes to confirm the installation and this will now install NSX packages on all our esx hosts in cluster.
I will now repeat the same on my other cluster as well so we can create transport zones later to move workloads between both our clusters.
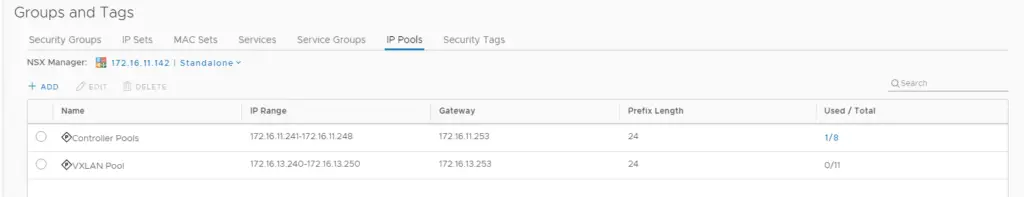
Configuring VXLAN Pool
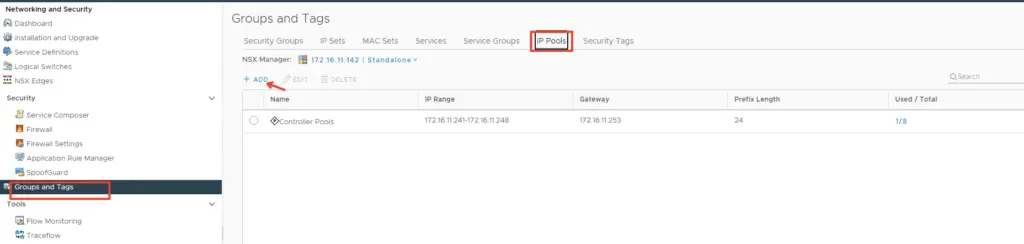
At this stage, we will need to now enable VXLAN so we will require a new IP Pool for VXLAN vmkernel IP’s
Go to Groups and Tags > Select IP Pools > Add new IP Pool
Choose Add IP Pool to assign the IP for the VTEP or VXLAN traffic. VLAN I’ll be using for VXLAN is 1613
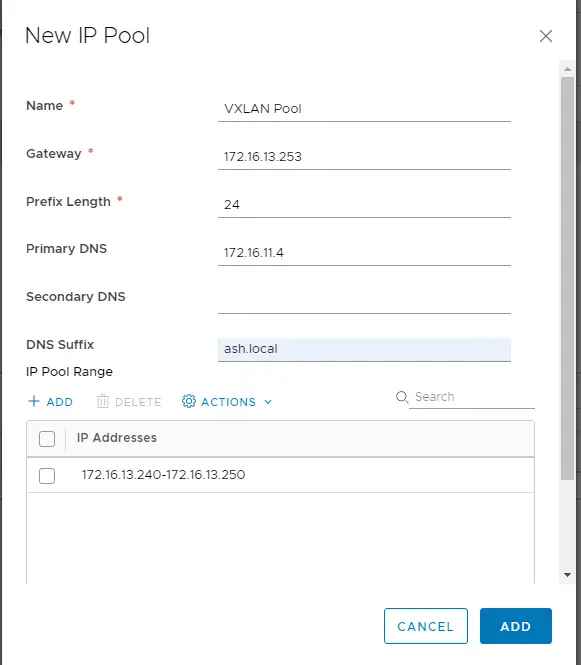
Once the VXLan pool is defined, we will have an entry as below showing the IP range for our VTEP
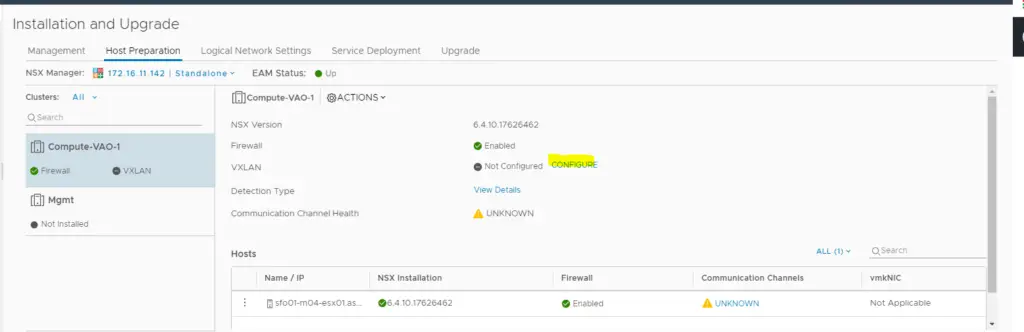
At this stage, all we have now to do is configure the VXLAN on the cluster. Click Host Preparation > Select Cluster > Configure VXLAN
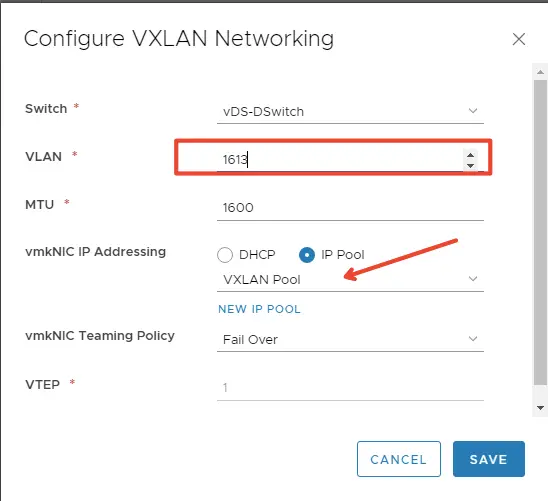
Configure VXLAN networking as shown and click Save
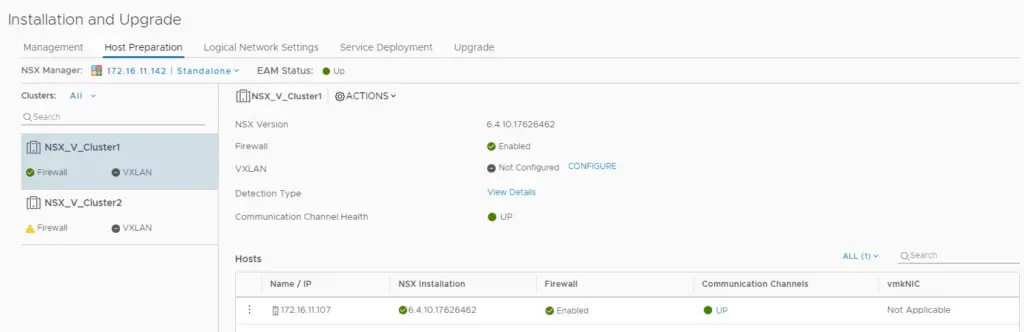
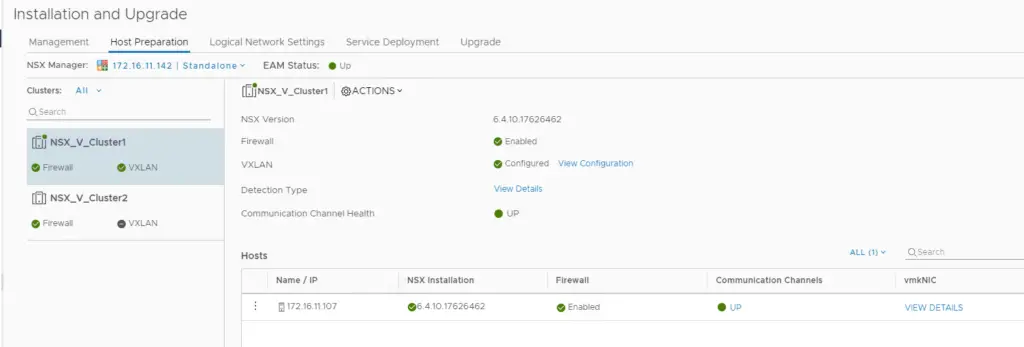
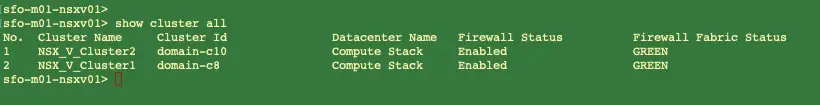
Once the configuration is complete, we should find the firewall, VXLAN and the communication channel health is up and showing green.
This new vmkernel port on the esxi host shows the host is ready to accept VXLAN traffic. This vmk1 adapter responsible for encapsulating VM traffic inside of a VXLAN header and routing the packet to a destination VTEP IP.
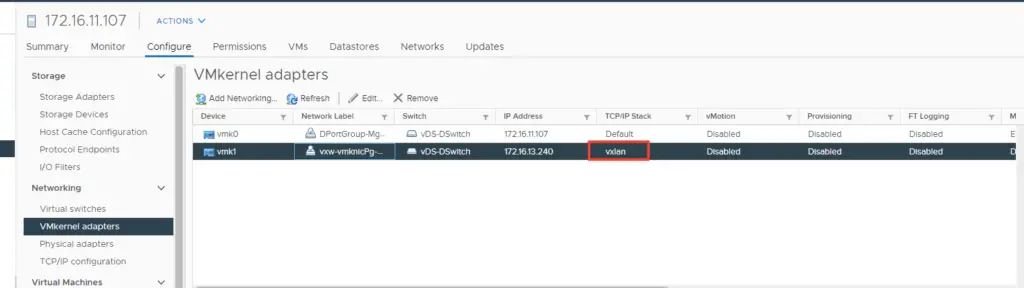
Prepare new ESXi Hosts for the NSX
Place the host in maintainence mode, add the host to exisiting DVSwitch and drag the host into the cluster
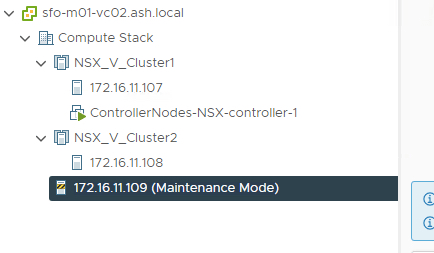
Once we will add any esx hosts to our cluster that’s enabled for NSX, automatically the VIB will be pushed to the new ESXI host and will configure it automatically. Similarly, once we remove a host from the cluster, it will uninstall all the NSX packages installed on the esx host
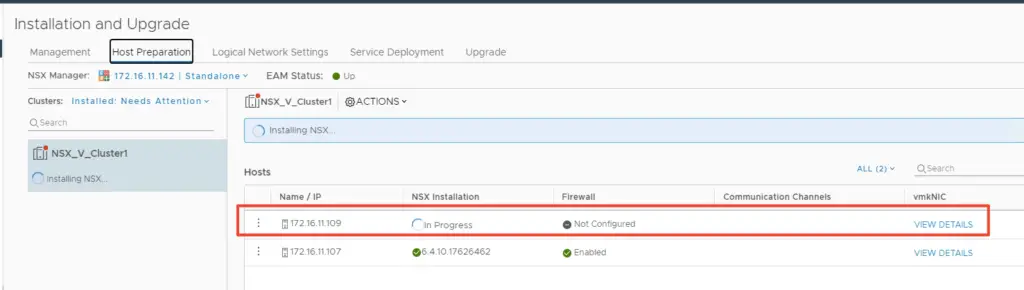
We should find the firewall, VXLAN and the communication channel health is up and green. Once its all green take the host off maintainence mode.
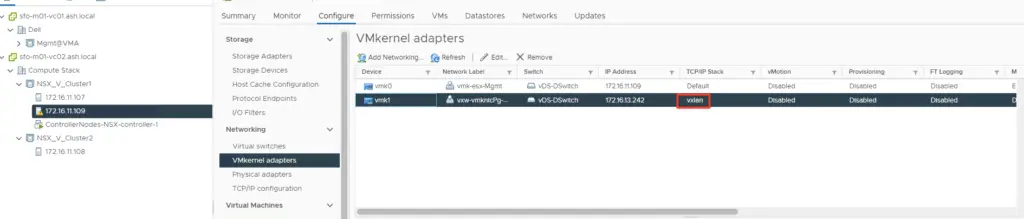
Verification of NSX-Manager Status after host preparation
Verification of NSX-VIB’s on esx hosts